When it comes to the world of science and working out, the connection isn’t always straightforward. From the bizarre to the bewildering, there’s a treasure trove of fascinating facts that peel back the layers of the science behind exercise. Whether you’re a fitness enthusiast or just curious about the quirkiest secrets of the gym, you’re about to embark on an enlightening journey through 17 weird and wonderful science facts that underscore the incredible complexity of the human body, the mind, and the gym. These facts will not only leave you sweating but also leave you with a sense of awe and wonder at the extraordinary mysteries behind working out. Now fasten your seat-belts (or, in this case, your sneakers) as we dive into the peculiar and profound science that makes exercise a captivating journey into the unknown.

Sweat Composition: The Science Behind Your Workout Scent
Did you know that the composition of sweat can vary, leading to distinct scents based on your activity? When you’re stressed or anxious, your sweat primarily consists of water and electrolytes, making it relatively odorless. However, when you’re engaged in a rigorous workout, your sweat contains a higher concentration of lipids, particularly fatty acids. These fatty acids, often associated with a less pleasant odor, play a critical role in your body’s cooling process. As you embark on a challenging exercise session, your sweat glands release moisture onto your skin’s surface, creating a cooling effect as it evaporates. The presence of fatty acids in exercise-induced sweat is an essential component of this natural cooling system. While the exact science behind the different aromas of sweat isn’t fully understood, it’s clear that the interaction of these fatty acids with the bacteria on your skin gives rise to a distinct fragrance.
This means that the next time you catch a whiff of your post-workout aroma, you can attribute it to the complex chemistry happening within your body. When it comes to body odor, it’s not just sweat; the microbes living on your skin also play a role in the equation. These microorganisms break down the various components of sweat, leading to the distinctive scent associated with body odor. Sweat itself primarily comprises water and electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium. However, when sweat mingles with bacteria, it can lead to the yellowish tint that can cling to your clothes. This interaction is a prime example of how our body’s natural processes can sometimes yield unexpected smells.

The Surprising Colorlessness of Sweat
Sweat is a universal experience during physical activity, and it’s commonly associated with body odor, especially in the context of a strenuous workout. One surprisingly unknown fact about sweat is that it is colorless. So, if it’s not the sweat itself that’s responsible for those unsightly yellow stains on your workout gear, what is? The culprit for those yellow stains is not the sweat itself, but rather the bacteria residing on your skin. These microscopic organisms break down the various components of sweat, leading to the discoloration that many of us have come to know. Sweat itself primarily comprises water and electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium.
Its main function is to regulate your body’s temperature by releasing moisture onto your skin’s surface, which then evaporates, creating a cooling effect. In addition to its cooling function, sweat also plays a crucial role in detoxifying the body by expelling waste products, making it a remarkable and multifaceted bodily process. However, when sweat mingles with bacteria, it can lead to the yellowish tint that can cling to your clothes. This relationship exposes how our body’s natural processes can sometimes yield unexpected and, at times, less than desirable results.

The Mystery of the Metallic Taste During Exercise
Picture this scenario: you’re in the midst of a rigorous workout, and suddenly, you detect a peculiar metallic taste in your mouth. This unexpected phenomenon, experienced by some individuals, is not entirely understood by scientists, but it may be linked to metabolic changes occurring during exercise. As you push your body to perform at its peak, a series of biochemical reactions unfold, causing alterations in the release and balance of various chemicals and electrolytes in your body. It’s within this intricate dance of physiological responses that the metallic taste might find its origin. Not everyone encounters this curious sensation, but for those who do, it serves as a reminder of the complexity of the biochemical processes that transpire within our bodies during physical exertion.
The metallic taste during exercise, though not fully explained, adds to the mosaic of physiological reactions that occur in response to physical activity. It’s an intriguing example of how our bodies can manifest unexpected sensations and experiences during the demanding moments of a workout. It also underscores the fact that exercise engages a complex interaction of chemical and physiological processes within our bodies, and the full extent of its effects may still hold surprises for science to unravel.

Coregasms: The Orgasmic Side of Exercise
Now, let’s delve into a truly unique exercise experience known as a coregasm. Some exercise enthusiasts, especially those who incorporate core-strengthening exercises like sit-ups or leg lifts, might be surprised to discover that they occasionally experience spontaneous orgasms during their workouts. The exact cause of this fascinating phenomenon is still not fully understood, but it is believed to be connected to the intense core engagement that occurs during these exercises. The theory goes that the increased activation of core muscles might indirectly stimulate the pelvic region, resulting in these unexpected sensations.
This unusual occurrence demonstrates how exercise can activate and awaken different parts of our body, including those we might not typically associate with physical activity. While it’s not a common experience, it highlights the profound connection between our muscles, nervous system, and physiological responses. For those who have encountered a coregasm, it’s a reminder that the human body can surprise us with unexpected sensations and experiences, even in the midst of a regular workout. It also showcases the intricate connection between different muscle groups and physiological responses, adding a layer of complexity and intrigue.
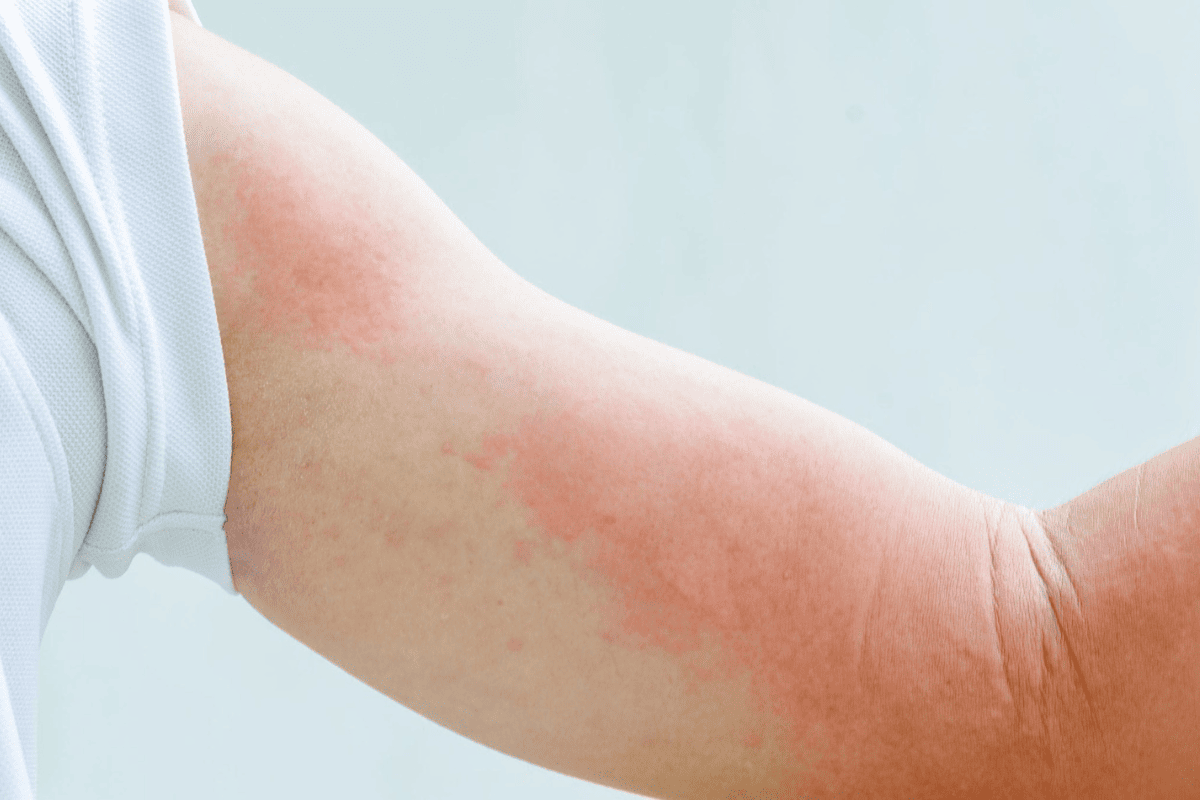
Exercise-Induced Hives: The Unexpected Skin Reaction to Physical Activity
Imagine engaging in physical activity but instead of feeling invigorated, you break out in hives, experience intense redness, and endure unbearable itching. This rare condition, known as exercise-induced urticaria, presents an intriguing but challenging aspect of exercise. The onset of symptoms can happen suddenly during exercise or shortly after. The affected individuals might experience not only the discomfort of hives but also redness and intense itching. While it’s not entirely clear why this phenomenon occurs, it is believed to involve a complex connection between immune system responses and exercise-induced changes in the body.
When you exercise, your body experiences a cascade of physiological reactions. In some cases, the immune system might misinterpret these changes as threats, leading to the development of hives and other allergic reactions. While exercise-induced urticaria is relatively uncommon, it serves as a reminder of the diverse ways our bodies can react to physical exertion. The intricacies of why some individuals develop exercise-induced urticaria while others do not are still not fully understood. It could be related to an underlying allergy or sensitivity to certain components in the environment or food, which is exacerbated by exercise-induced changes. Additionally, genetic factors and individual predispositions may also contribute to this condition’s development. The complexity of the human body is on full display when considering the interplay between exercise and the immune system, making exercise-induced urticaria a fascinating and somewhat enigmatic phenomenon.
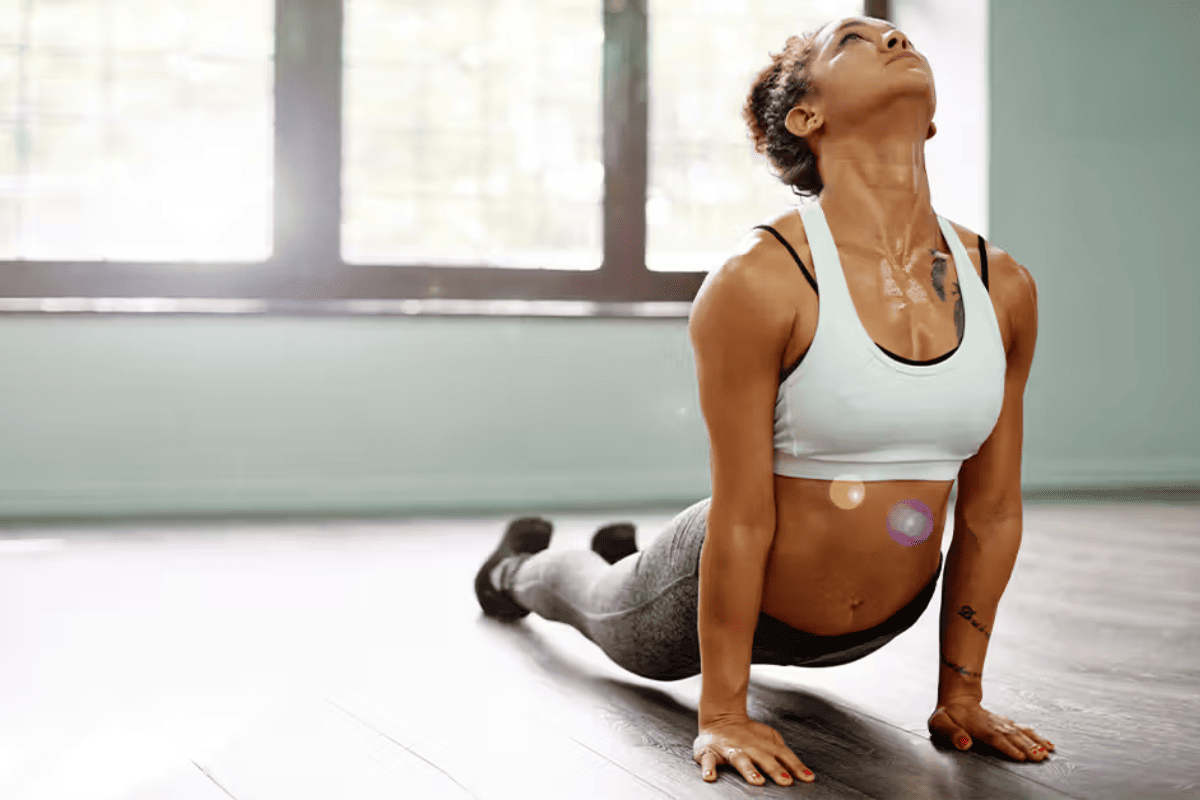

Hot Yoga’s Impact on Bone Density: A Surprising Benefit of Heat and Flexibility
For those who enjoy the practice of hot yoga, there’s more to it than just increased flexibility and relaxation. Recent research has suggested that hot yoga, which combines the benefits of yoga postures with a heated environment, might actually lead to increased bone density. This finding is particularly significant for reducing the risk of osteoporosis. Hot yoga combines heated surroundings with yoga postures, creating a challenging workout that can potentially boost bone density. The heat promotes better blood flow, allowing for deeper stretches, and the weight-bearing nature of the postures stimulates bone growth. This dynamic practice not only enhances flexibility and relaxation but also improves balance and coordination, reducing the risk of falls and fractures, especially in older adults.
The heat involved in hot yoga classes encourages the body to release stress hormones like cortisol can stimulate osteoblasts, the cells responsible for bone formation. Furthermore, the weight-bearing nature of many yoga postures promotes the development of bone density. The combination of heat and weight-bearing postures creates an ideal environment for bone health, providing yet another reason to roll out your yoga mat in a hot studio. This exciting revelation adds a new dimension to the benefits of yoga and heat therapy, showcasing the potential for holistic health improvements through physical activity. It emphasizes that exercise is not only about muscle strength but can also significantly impact the structure and health of our bones, making it a multifaceted approach to overall well-being.
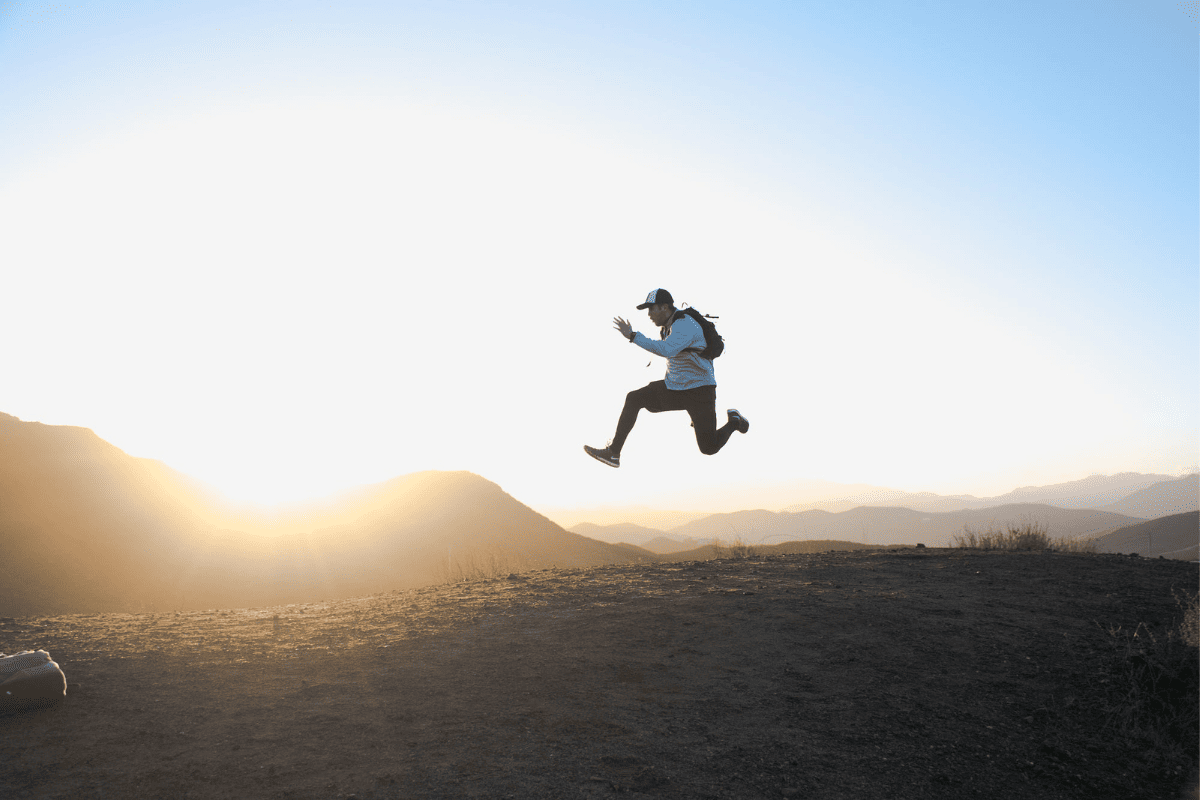

The Runner’s High: When Exercise and Endocannabinoids Combine
Long-distance runners often speak of experiencing a euphoric sensation known as the “runner’s high.” This phenomenon is characterized by feelings of euphoria, reduced pain perception, and an improved overall mood during and after a strenuous run. While it may seem like a mere byproduct of intense exercise, there’s more to it than meets the eye. The runner’s high is believed to be linked to the release of endocannabinoids, which are compounds similar to those found in marijuana. These natural substances interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system, a complex network of receptors and molecules, which plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes.
During a challenging run, the body responds by releasing these endocannabinoids, leading to a range of effects that contribute to the euphoria experienced by many runners. The endocannabinoid system is involved in mood regulation, pain perception, and overall well-being. Its activation during exercise adds an extra layer of enjoyment to the activity. The runner’s high connection to the endocannabinoid system, illustrates the profound effects of exercise on our brain chemistry and mental well-being. It emphasizes the capacity of the human body to produce natural mood-enhancing compounds during physical activity, making the runner’s high a fascinating window into the symbiotic relationship between exercise and the brain.

Gym Chills: The Paradox of Cooling While Sweating
For some individuals, a workout at the gym can trigger an unusual sensation – chills or goosebumps. What’s curious about this experience is that it can occur even when you’re sweating profusely. The connection between sweating and getting the chills might seem paradoxical, but it can be explained by the rapid cooling of the skin. As your body temperature rises during exercise, sweat is produced as a means of cooling you down. However, when the sweat evaporates quickly, especially in environments with high air circulation or low humidity, it creates a cooling effect on your skin. This rapid cooling can result in chills, even though you’re actively engaged in an activity that typically raises body temperature.
The next time you find yourself working up a sweat with goosebumps, know that it’s a consequence of your body’s efficient cooling mechanism. It’s a reminder that the human body is a finely tuned instrument, capable of responding to a variety of environmental conditions and internal changes during exercise. This curious phenomenon also exposes the dynamic cooperation between your body’s cooling mechanisms and its efforts to maintain an optimal internal temperature. It adds a layer of intrigue to the gym experience, reminding us that our bodies are adaptable and responsive in a multitude of ways, even in the seemingly contradictory context of chills amidst a heated workout.
Exercise-Induced Lactation: A Peculiar Side Effect of Physical Activity
It’s rare, but it happens: some women who engage in strenuous exercise find that it stimulates lactation, even if they are neither pregnant nor breastfeeding. While this might seem like an unusual side effect, it provides insight into the complex relationship between exercise and hormones in the human body. The exact cause of exercise-induced lactation remains a topic of ongoing research, but it’s thought to involve the hormonal changes that occur during intense physical activity. Certain hormones, particularly prolactin, which is associated with milk production, can become elevated during strenuous exercise.
This unique phenomenon of exercise-induced lactation serves as a fascinating example of the body’s adaptability under various conditions. The female body’s ability to produce milk under strange circumstances emphasizes the intricate interplay between hormones, exercise, and physiological responses. It is a reminder that exercise can have a profound impact on the body’s hormonal balance and reproductive system, even in surprising and unexpected ways. Understanding these intricate relationships can lead to more insights into the complexities of the human body and how it responds to the demands we place on it during physical activity.
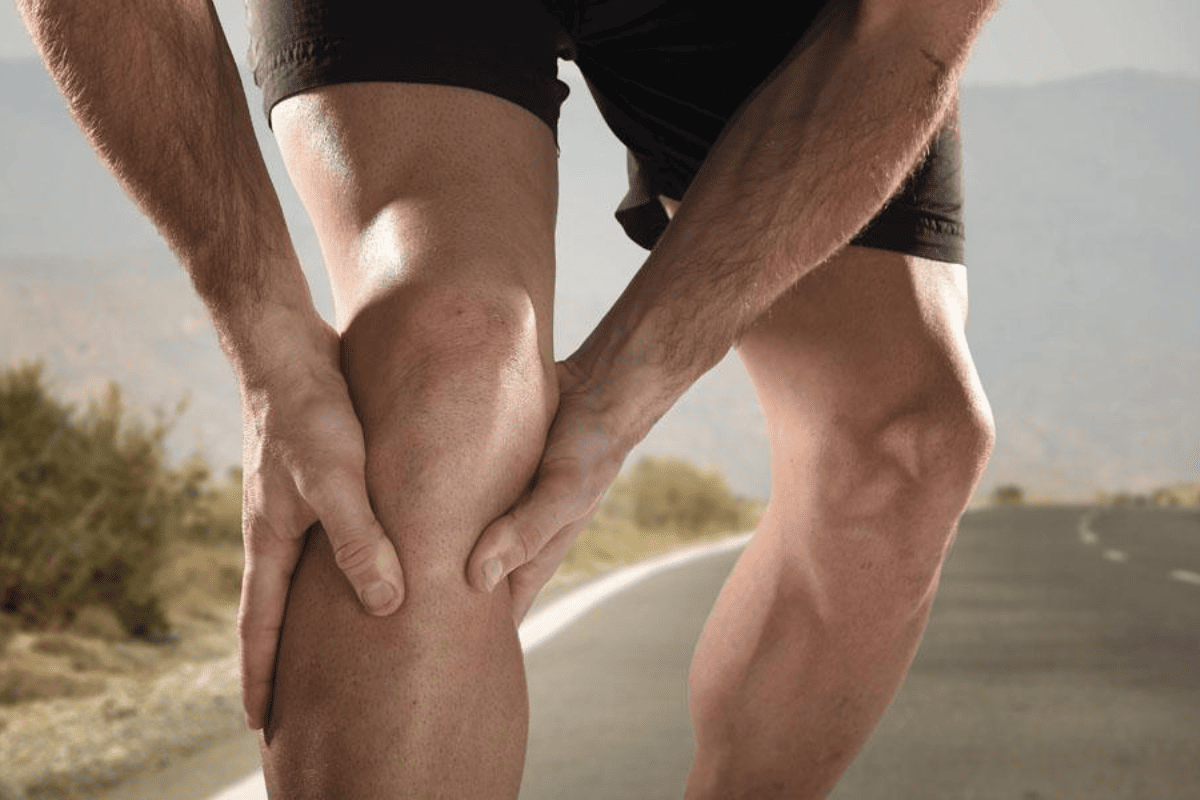

Joint Lubrication: The Body’s Built-In Mechanism for Joint Health
Exercise is not just about building muscle; it also plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of your joints. One fascinating aspect of this is the increased production of synovial fluid within your joints during physical activity. This synovial fluid acts as a natural lubricant, reducing friction between the various components of your joints and enhancing their flexibility. This natural lubrication process not only aids in reducing the risk of joint injuries but also supports overall joint health and longevity, boasting the multifaceted benefits of regular exercise.
When you engage in activities like walking or running, the mechanical stress placed on your joints triggers the release of synovial fluid. This process helps ensure that the components of your joints, such as cartilage and ligaments, move smoothly and without discomfort. It’s a fascinating example of how the body’s design includes built-in mechanisms to support physical activity and maintain joint health. Joint lubrication plays a crucial role in ensuring that your joints function optimally, whether you’re taking a leisurely stroll or engaged in more intense activities. It’s a reminder that exercise is not just about building and toning muscles but also about preserving the intricate machinery of your joints. By maintaining healthy joints, you can continue to move with ease and comfort, both in your daily life and during your workout routines.
Elevated Pain Threshold: The Power of Endorphins
A heightened tolerance for pain is an intriguing adaptation that distinguishes experienced athletes from beginners. As you work up a sweat during exercise, your body releases a remarkable class of natural pain relievers known as endorphins. These endorphins are often referred to as “feel-good” hormones because they not only improve your mood but also elevate your pain threshold. In simple terms, they make it easier for you to endure discomfort and push through challenging moments during your workout.
The release of endorphins is a key part of the body’s response to exercise. When you engage in physical activity, especially during vigorous efforts, your body may experience a temporary state of stress or discomfort. To help you cope with this stress, your brain releases endorphins. These remarkable compounds bind to specific receptors in your brain, effectively blocking the transmission of pain signals and creating a sense of euphoria. The result is that you can persevere through intense exercise with a reduced perception of pain, and even enjoy the process. This phenomenon serves as a reminder of the incredible ways in which the body adapts to meet the challenges it encounters, and how exercise can be a source of not only physical but also mental resilience.
Reduced Resting Heart Rate: A True Hallmark of Fitness
In the pursuit of a healthier heart and a more robust cardiovascular system, there’s one adaptation that’s a true hallmark of fitness: a reduced resting heart rate. The heart, that tireless muscle pumping life throughout your body, becomes so efficient that it doesn’t need to work as hard when you’re at rest. A lower resting heart rate is not only a sign of cardiovascular fitness but also an indicator of improved heart efficiency, as it can pump the same amount of blood with fewer beats, reducing the overall workload on this vital organ. This remarkable feat of adaptation results from regular exercise and physical conditioning, where the heart evolves to excel at delivering oxygen and nutrients to your body’s tissues.
When you engage in aerobic activities like running, swimming, or cycling, your heart undergoes a transformation. It becomes a well-oiled machine, making your workouts more efficient and your health more robust. This lower resting heart rate is not just a mere number on your fitness tracker; it’s a key indicator of cardiovascular fitness. It’s associated with a reduced risk of heart diseases, and it’s the hallmark of improved cardiovascular endurance. Athletes and regular exercisers often flaunt a lower resting heart rate, showcasing their hard-earned fitness level. This adaptation showcases the heart’s ability to adapt and respond to the demands of physical activity, ensuring that it operates optimally while at rest and during exercise. It’s a testimony to the incredible plasticity of the human cardiovascular system, reminding us that consistent physical training and conditioning can bring about remarkable changes in our bodies.
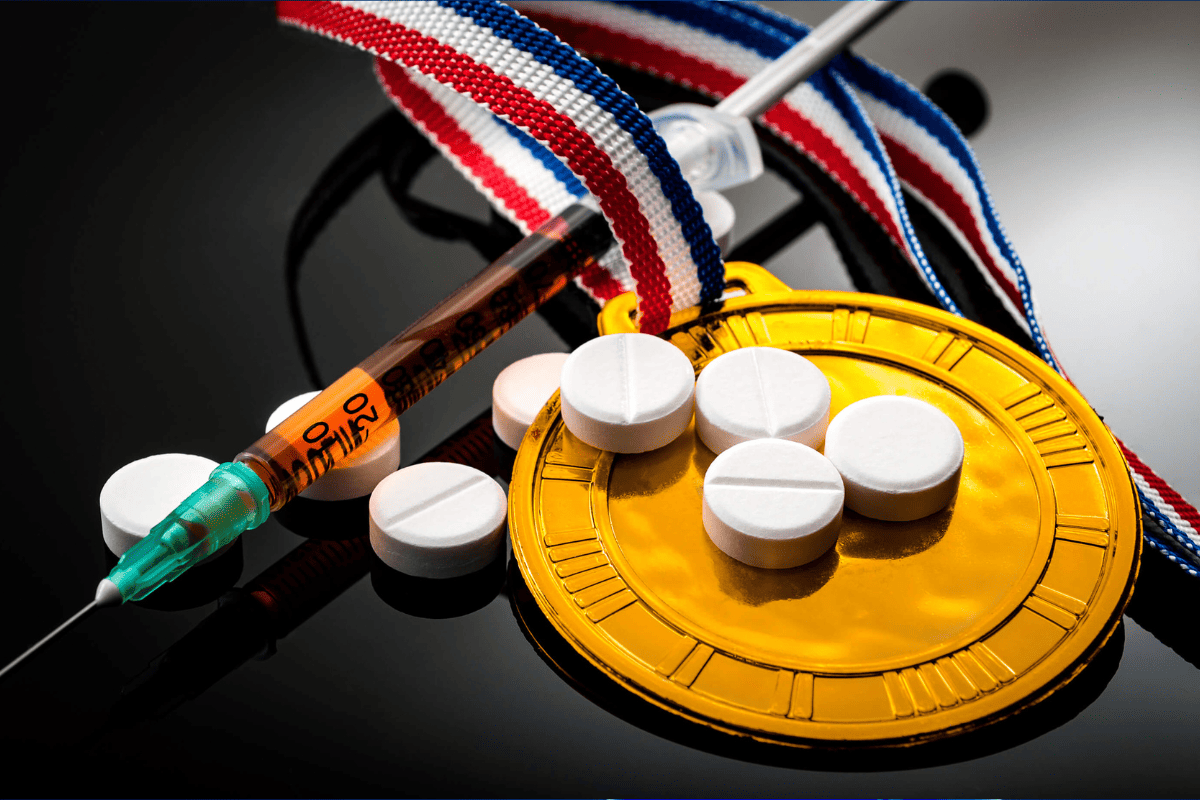

Exercise and EPO: The Dark Side of Athletic Performance
Perpetually striving for athletic perfection unveils the human body’s intricate adaptations, consistently surprising us. One such remarkable phenomenon unfolds during intense physical activity when your body releases a hormone called erythropoietin (EPO) from the kidneys. EPO is a naturally occurring substance that plays a pivotal role in regulating the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow. This response is essential for athletes as it results in the creation of additional red blood cells, a process known as erythropoiesis. These extra red blood cells are like an oxygen-rich army, rushing through your circulatory system to deliver more oxygen to hardworking muscles. This boost in oxygen supply enhances endurance, stamina, and overall athletic performance. In a sense, it’s a natural, built-in performance enhancer that helps athletes push their limits.
What makes this biological process even more intriguing is the dark side it has cast upon the world of sports. In extreme cases, some athletes have attempted to artificially manipulate their EPO levels by using synthetic EPO, a practice commonly referred to as blood doping. This underhanded method is banned in most competitive sports due to the potential risks it poses. When athletes artificially increase their red blood cell count, it can lead to a condition called polycythemia, characterized by an excessive production of red blood cells, which can strain the circulatory system and pose serious health risks. Moreover, it raises ethical concerns, as it provides an unfair advantage in the sporting arena and threatens the integrity of competitive athletics. While EPO naturally empowers athletes, its artificial manipulation underscores the fine line between pushing the boundaries of human performance and crossing into dangerous and unethical territory.

Unlocking the Power of the Gut: How Physical Activity Shapes Your Gut Health
We often focus on the visible benefits of exercise like toned muscles and improved cardiovascular health. But beneath the surface, there’s a hidden gem of well-being that’s just as crucial – the gut microbiome. This microscopic ecosystem that harbors trillions of microorganisms is nestled in our digestive system. It’s a bustling community of bacteria, viruses, and fungi that silently orchestrate vital processes, influencing digestion, metabolism, and even immune function. Recent research has unveiled the remarkable connection between exercise and the gut microbiota.
When you commit to regular physical activity, you’re creating a welcoming environment for beneficial bacteria to thrive. These tiny heroes break down food, produce essential nutrients, and shield your gut from harmful pathogens. As their numbers multiply, harmful microorganisms find it increasingly difficult to establish a foothold in your gut, leading to improved digestive health. But there’s more to the story. Exercise also triggers the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in your colon. These SCFAs are essential for maintaining a robust intestinal barrier, reducing inflammation, and overall gastrointestinal health. This not only enhances digestion and nutrient absorption but also contributes to a happier and healthier gut. When you lace up your sneakers, remember that you’re not only sculpting your physique but nurturing a hidden ecosystem within, where the balance between physical activity and gut health paves the way for a vibrant and healthier life.

Muscle Memory: A Remarkable Phenomenon
Muscle memory is a phenomenon that leaves athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and rehabilitation patients astounded by the human body’s ability to bounce back. This remarkable adaptation allows muscles to regain strength and coordination more rapidly after a period of disuse or injury. The secret to muscle memory lies in the concept of neuromuscular memory, where the brain and nervous system retain motor skills and movement patterns acquired through training.
When you engage in regular physical training or learn specific movements, your brain creates neural pathways that become ingrained in memory. These pathways store the correct muscle activation patterns and movement sequences associated with the exercises or skills you’ve practiced. What’s truly remarkable is that even after a period of inactivity or injury, your brain can reactivate these neural pathways more efficiently than when you initially learned the skill. This leads to a faster reclaiming of the physical skill, and your muscles seem to remember what they once knew.
Earwax and Exercise: The Unanticipated Earwax Connection
The relationship between earwax and post-workout body odor is an unexpected and intriguing scientific discovery. Recent research has unveiled a surprising link between the type of earwax an individual possesses and their propensity for body odor during exercise, shedding light on an often overlooked facet of our biological makeup. This intriguing connection reveals that earwax can significantly influence the intensity and nature of the body odor experienced during and after physical exertion. Wet earwax contains a higher proportion of lipids and fatty acids, these components serve as protective and lubricating agents in the ear canal. This discovery displays the intricate nature of our body’s chemistry and how seemingly unrelated factors can converge to produce interesting and sometimes surprising outcomes.
This correlation between earwax type and post-exercise body odor opens a new window into the complexity of our genetic makeup and how it affects our everyday experiences. It serves as a testament to the fascinating connection between our unique traits and functions, showcasing how even something as seemingly minor as the composition of our earwax can exert a tangible influence on our lives. Just remember when you ponder the source of your post-workout scent, consider the role that your earwax type plays in this intriguing olfactory puzzle, illustrating the remarkable complexity of the human body’s interconnected nature.

Exercise and Enhanced Olfactory Sensitivity: A Surprising Benefit
A surprising revelation has come to light: engaging in consistent physical activity can notably amplify your sense of smell. This means that beyond its well-known physical and mental health benefits, exercise might also boost your olfactory sensitivity, making your sense of smell more acute than before. Research has shown that individuals who engage in consistent physical activity exhibit an improved ability to detect and differentiate odors. While the exact mechanisms behind this phenomenon are not entirely understood, it is believed that exercise might enhance blood flow and oxygen delivery to the olfactory receptors in the nose, thus making them more responsive.
This intriguing link between exercise and olfactory enhancement adds a new dimension to the benefits of staying active, showing how taking care of your body through physical activity can offer unexpected advantages, such as a keener sense of smell. So, in the future you can savor the thought that your exercise routine may be heightening your ability to appreciate the world of scents in ways you never imagined. As science continues to explore the multifaceted benefits of exercise, this connection between physical activity and olfactory sensitivity reminds us that a healthier, more vibrant life is often accompanied by delightful surprises in unexpected places, such as the human nose.
Where Do We Find This Stuff? Here Are Our Sources:
Sweat Composition: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6773238/
Sweat Colorlessness: https://www.hyperhidrosiscumc.com/13-fun-facts-about-sweat/
Metallic Taste: https://www.outsideonline.com/health/training-performance/why-do-i-get-metallic-taste-my-mouth-during-intense-exercise/
Coregasms: https://www.verywellfit.com/what-is-a-coregasm-5095046
Exercise induced hives: https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2001/1015/p1374.html
Yoga and bone density: https://yogainternational.com/article/view/yoga-and-osteoporosis-the-dos-and-donts/
Runners High: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35081831/
Workout Chill: https://www.livestrong.com/article/424173-body-starts-chilling-after-workout/
Exercise Induced Lactation: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/22429-prolactin
Joint Lubrication: https://www.physio-pedia.com/Synovium_%26_Synovial_Fluid
Elevated Pain Threshold: https://www.webmd.com/depression/exercise-depression
Reduced Resting Heart Rate: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6306777/
Exercise and EPO: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7213874/
Gut Health: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5357536/
Muscle Memory: https://blog.nasm.org/muscle-memory
Earwax and Exercise: https://atlasbiomed.com/blog/sweat-and-body-odour/
Exercise and Enhanced Olfactory Sensitivity: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/medrxiv/early/2022/09/30/2022.09.30.22280564.full.pdf
