Ever wonder how old your furry friend really is? Beyond their chronological age lies a human-equivalent, revealing their stage in life. Our Dog Age Calculator unlocks this mystery, translating your dog’s age into human years based on size and breed. Discover if your playful pup is a toddler, your steady companion a middle-aged adult, or your senior dog a wise elder. Unravel the secrets of your dog’s age and gain deeper insights into their behavior and needs.
A dog’s age is more than just a number. It provides insight into their physiological needs, health status, and even their behavior. But have you ever wondered how to translate your dog’s age into human years?
Discover the age of your furry friend with our Dog Age Calculator. By providing key details about your dog, such as gender, breed, and age, our advanced algorithm generates a tailored estimate. Please note that this estimate is based on the information you provide, offering a reliable approximation.
This guide will unravel the intricacies of canine aging, providing valuable insights for pet owners everywhere.
Use this calculator on your site!
Powered by World Animal Foundation
Copy Embed Code
Instructions
1. Copy the code above.
2. Add it to your post/page where you want to show the calculator.
3. Change the size using the iframe’s width and height if needed.
4. You must provide credit to use the calculator.
What is the 1:7 Rule of Calculating Dog Age?
One of the most common methods people used, since the 1950s, to calculate a dog’s age in human years was the ‘1:7 rule’. According to this traditional method, each year of a dog’s life is equivalent to roughly seven human years.
The origin of this formula can be traced back to the notion that the 7:1 ratio was derived from the average human life expectancy of 70 years and the average lifespan of dogs, which was believed to be around 10 years.
However, recent studies suggest that this approach oversimplifies the aging process of dogs. Aging in dogs is more complex and varies depending on their size, breed, and overall health.
How to Calculate Dog Age to Human Years
To accurately calculate your dog’s age in human years, we must look beyond the ‘1:7 rule’. According to American Veterinary Medical Association:
- When comparing human and dog ages, a common understanding is that the first year of a medium-sized dog’s life equals 15 human years approximately.
- The second year of a dog’s life corresponds to about nine years for a human. By the time they reach their second year, it’s as if they’ve lived for around 24 human years.
- Subsequently, each additional human year is estimated to be equivalent to about five years in a dog’s life.
However, it’s important to note that the aging process can vary among individual dogs and different dog breeds. Factors such as size, genetics, and overall health can influence the rate at which dogs age.
Thus, a more nuanced calculation provides a more accurate reflection of your dog’s life stage.
How do Researchers Determine These Numerical Values
Researchers determine the numerical values to determine dog age in human years based on various factors and studies. The underlying basis for these numerical values stems from observing the developmental milestones in dogs. Dogs pass through five life stages—puppy, young adult, mature adult, senior, and end of life.
People and dogs age at very different rates. Moreover, humans live longer than dogs.
One common approach involves comparing the aging processes and life expectancies of dogs and humans. By examining the average lifespan of different dog breeds and how their bodies age compared to humans, researchers can establish approximate equivalences between dog and human age.
The dog stages have corresponding developmental stages in human life, which is how researchers establish these values. Moreover, scientific methods, like studying patterns of DNA methylation (a marker of biological aging), provide more precise ways to determine the true age of your dog in human years.
However, it’s important to acknowledge that these numerical values are rough estimate and can vary between individual dogs and breeds.
Why Small Dogs Have Longer Lifespans than Large Dogs
Smaller dog breeds generally have longer lifespans compared to larger dogs, which seems counterintuitive if we consider the general pattern in the animal kingdom, where larger species often live longer. The reason behind this intriguing aspect of canine aging involves a combination of genetics, development, and physiology.
Firstly, the growth and development rates play a significant role in a dog’s lifespan. Larger breeds tend to grow quickly and age faster. These dogs mature and reach adulthood more rapidly, and with this accelerated growth, they also experience age-related illnesses sooner.
Large breeds are more prone to health problems such as hip dysplasia, cancer, and heart diseases, which can decrease their overall lifespan. Larger dogs undergo a rapid progression from puppyhood to adulthood, increasing the risk of abnormal cell growth, and other diseases.
Secondly, the metabolism rates differ in small and large dogs. Smaller dogs have faster metabolic rates, leading to higher energy needs per unit of body weight. This faster metabolism seems to contribute to a slower aging process, hence a longer lifespan.
Lastly, genetics plays a critical role. The genes that control size also appear to influence aging and disease propensity in dogs. Certain genetic predispositions to diseases are more common in large dog breeds, contributing to their shorter lifespans.
According to AKC, here are the average lifespans of different breeds on the basis of their size:
- Small or toy breeds (less than 20 pounds): 8 to 11 years
- Medium dog breeds (20 to 50 pounds): 8 to 10 years
- Large breeds (50 to 90 pounds): 8 to 9 years
- Giant breeds (more than 90 pounds): 6 to 7 years
Here is a list of some popular dog breeds, along with their average age:
| Cavalier king charles spaniel | 12-15 years |
| Bernese mountain dog | 6-8 years |
| Jack russell terrier | 13-16 years |
| Boston terrier | 13-15 years |
| Shih tzu | 10-16 years |
| Bichon frise | 12-15 years |
| Australian shepherd | 13-15 years |
| lhasa apso | 12-14 years |
| Shetland sheepdog | 12-13 years |
| English bulldog | 8-10 years |
| Chihuahua | 12-20 years |
| Poodle | 12-15 years |
| Pomeranian | 12-16 years |
| Dachshund | 12-16 years |
| Newfoundland | 8-10 years |
| Bernard | 8-10 years |
Different Dog Breeds Age at Different Rates
Different dog breeds age at different rates due to various factors, including dog DNA, size, and overall health. As discussed above, small dog breeds tend to have longer lifespans compared to larger breeds.
Additionally, it’s crucial to note that a dog’s breed isn’t the only determinant of a dog’s life expectancy. Factors such as diet, exercise, healthcare, and living environment also have a significant impact on the length and quality of a dog’s life.
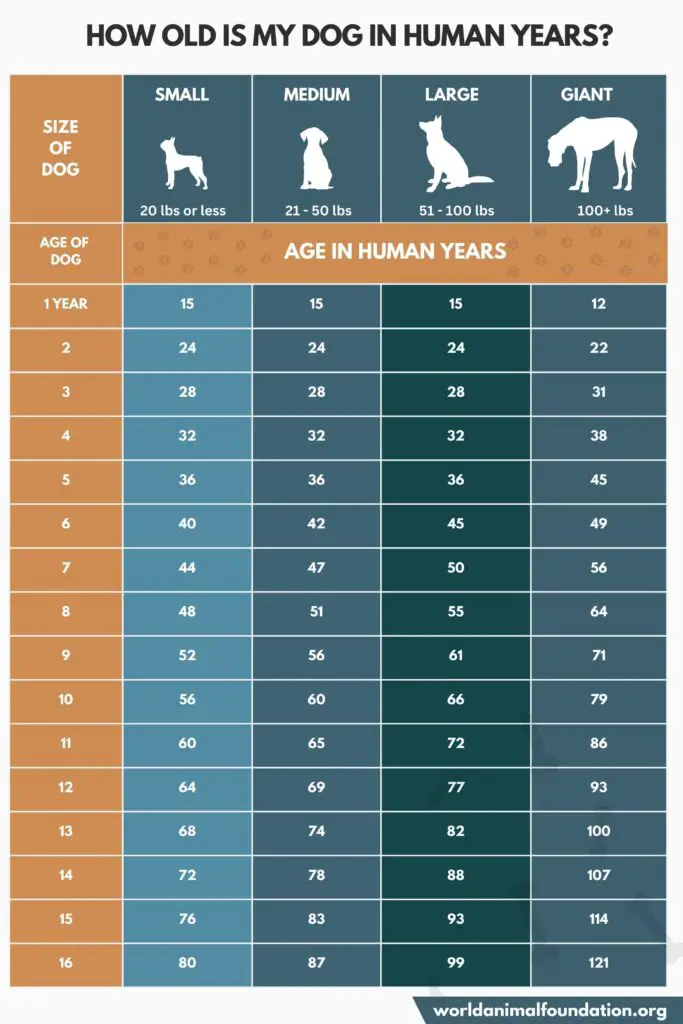
Refer to the following dog age chart to compare the developmental and aging stages of dog years to human years based on their size (small, medium, large, giant). This resource will provide estimates into your dog’s current stage of development/aging.
Regular veterinary check-ups and providing a nurturing environment are essential for ensuring the best possible quality of life for dogs of all breeds.
Epigenetic Clock Study
An epigenetic clock serves as a biochemical test utilizing DNA methylation levels to measure an individual’s age accurately.
Scientists have examined the shared methylation changes in human vs. dog genomes as they age, shedding light on the conserved physiological stages all mammals experience, from early development to aging and death.
By analyzing the methylation changes in the genomes of both dogs and humans as they age, researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine, discovered shared age-related alterations, particularly affecting developmental gene networks.
Utilizing this information, they developed a formula that enables a more precise comparison of age between humans and dogs.
Advantages of Knowing Your Dog’s Age in Human Years
Knowing your dog’s age in equivalent human years is more than a fun fact. It provides a wealth of information that can significantly impact the quality of your pet’s life. Here are some key advantages:
1. Healthcare Decisions: Puppies need different care than adolescent dogs and adult dogs have different needs than seniors. Regular check-ups, vaccinations, and preventive treatments for conditions more prevalent in certain life stages can be scheduled accurately.
2. Dietary Considerations: A dog’s nutritional needs change with age. Puppies require a diet high in protein for their fast growth, while senior dogs may need fewer calories but more fiber and certain nutrients.
3. Exercise and Training: Different ages come with different energy levels and learning capabilities. Converting your dog years to human years can help set realistic expectations for training and guide suitable levels of exercise.
4. Behavioral Expectations: Just as human behavior changes with age, so does a dog’s. Adolescence in dogs, like in humans, is often a time of testing boundaries and newfound independence. Senior dogs, on the other hand, might require more rest and patience.
5. Preventive Health Measures: Awareness of your dog years in human years can help you anticipate and prevent age-related health issues. For instance, older dogs may benefit from regular screenings for common conditions like arthritis or diabetes.
By better understanding your dog’s age in human years, you can be more attuned to their needs, helping your dogs live a healthier and happier life.
FAQs
What are dog years?
Dog years refer to the equivalent age of a dog in terms of a human lifespan.
How to calculate the lifespan of a mixed dog breed?
Determining the lifespan of a mixed-breed dog can be tricky as it involves considering the average lifespan of each parent breed and its size. This is because the lifespan of a dog is influenced by the traits of its various breeds, along with other factors like overall health, diet, and care
Conclusion
Understanding your canine friend’s age in human years offers insight into their health, needs, and life stage. By considering factors such as breed, size, and genetic traits, we can better appreciate our dogs’ lifespans and provide them the care they deserve in each stage of their lives.
The “dog years” calculation, while a fun comparison, isn’t a precise measure of a dog’s physiological age. It provides a general idea of their developmental stage relative to humans, acknowledging their faster initial growth and subsequent varying aging rates depending on breed and size. Understanding a dog’s life stage through observation, veterinary checkups, and awareness of breed-specific lifespans offers a more accurate picture of their health and anticipated needs. Ultimately, cherishing each stage of a dog’s life, regardless of the “human year” equivalent, is what truly matters.