Every year, our technology advances further. From phones to vacuums, computers are everywhere. We have become good at using robots for daily tasks without even thinking about it. Nowadays, we frequently use artificial intelligence to solve problems. In fact, artificial intelligence can develop solutions that the human mind and body cannot do quickly or are incapable of doing at all. We used to have to build homes by hand; now, we have robots capable of making entire houses in a single day. Say goodbye to cleaning and sanitizing hospital rooms and other areas with back-breaking labor. Thanks to artificial intelligence, we can use a powerful light for an even better cleaning effect than before.
Finally, we have vehicles that can drive you from one location to another without anyone touching the steering wheel. This year, AI creates enhanced therapy with artificial pets who can learn their own name and set sleep patterns. We can even construct the essential elements of our cells to see what proteins may look like. Let’s take a quick look at what artificial intelligence can do within the last year. Here are 20 AI updates from 2021.

20. Hadrian X is changing the way we build our homes and commercial buildings.
Fastbrick Robotics first tested its creation in 2015, and that’s when Hadrian X changed everything. This artificial intelligence demonstrated to have a bricklaying rate of 225 bricks per hour. Since then, with modern improvements in its AI and other components, Harian X can lay over 1,000 bricks per hour (via Wikipedia). Essentially, this machine could build an entire two-bedroom, one-bathroom house during one average shift. This speed and accuracy will radically change how we can build homes, as this machine can work 24 hours a day without breaks in most kinds of weather. It doesn’t even need to wait for the mortar between the bricks to dry, as it uses a polyurethane adhesive to bind everything together. This adhesive dries within 45 minutes and has better thermal and strength properties than traditional brick mortar has.
Currently, the Hadrian X is in Willagee, Western Australia, where it is working on its largest project to date – building the walls for 16 Townhouses. It uses blocks equivalent to 12 standard construction bricks. Furthermore, it can lay a single block every 30 seconds. They estimate this new project will cut projection time by over 70% compared to a regular crew of bricklayers (via Wikipedia). Though it is not commercially available yet, it is easy to see how much time and money this AI project can save building companies.

19. The “Saul Robot” can sterilize entire rooms with little help from humans.
With Covid-19 affecting lives all across the globe, the robot nicknamed Saul can help keep essential areas in hospitals and other locations with delicate equipment as clean as possible. According to Xenex, the robot’s creator, it is capable of destroying the SARS-CoV-2 virus (and many other pathogens) with up to 99.99% deactivation rates. It utilizes high-end ultraviolet lights, which are 25,000 times more potent than a regular fluorescent light (via Xenex). All surfaces that the light can reach become disinfected within five minutes of exposure. They also tested this robot in hospitals for Ebola. What did they discover? The studies revealed this artificial intelligence could help reduce infection rates by a massive 60%.
The newest iterations of this robot are called LightStrike (via DIYA Labs). It can destroy SARS-CoV-2 viruses within 2 minutes using a process of high-intensity bursts of a pulsed xenon lamp. Since this light is harmless to surface areas, machinery, and materials, you can safely use it in all kinds of places. Inventors created this robot to disinfect hospital rooms. Nevertheless, convention centers, prisons, airports, sports areas, schools, and many other places where COVID-19 may be readily transmissible also use it.

18. Quantum computing will become even more present in our lives.
You don’t need an advanced degree in quantum theory to see how this phenomenon can potentially impact our everyday lives. At its core, this will allow technology to be faster and more accurate than ever before. It will help us build better, more responsive robotics that emulates human characteristics. Quantum computing can help us compute data, allowing medical sciences to study and combat diseases faster and more accurately (via Wikipedia). Furthermore, it can help us design better vehicles and reduce pollution from excess waste by building better computer models.
Quantum computing uses information data called “qubits” in the same way that modern computers use data called “bits.” The difference here is that regular bits can be in 2 states of existence, 0 and 1 (via Wikipedia). However, qubits can exist as either 0 or 1 somewhere between those two states, which scientists call “superposition.” What will make quantum computing so much faster? Qubits can hold twice as much data as a regular bit can hold using a process called superdense coding.
17. People use artificial intelligence to generate images simply from a text description.
DALL·E is a new AI language model trained to take text-based descriptions and turn them into actual images (via Technology Review). Similar to the way we can say to you, “A brown dog that is sleeping” will conjure up a picture in your mind of a sleeping brown dog; DALL-E uses an extensive neural networking system to do the same thing (via Technology Review). It is even capable of creating anthropomorphized images. What does that mean? If you say create “an illustration of a baby daikon radish in a tutu walking a dog” then it will provide pictures of precisely that.
The AI here works by combining the text data and the image data as a single stream of data using what is called tokens. Each token is part of the program’s vocabulary (imagine each letter of the English alphabet represented as a token to get the idea) which means both text and image portions. Using this concept, the artificial intelligence can generate an image entirely from scratch or even alter an existing image to fit the required data.

16. AI can be used to make new music from artists long gone.
Utilizing an open-sourced AI program called Magenta, created by Google, the project known as Lost Tapes of the 27 Club was able to create new music in the famed styles of various artists (via Billboard). They have done this by using Magenta to analyze up to 30 songs from each musician, which then takes similarities from those songs and creates a blend of skills and stylistic designs to create a “new song” that closely resembles that artist’s previous music. In this case, they made a song called “Drowned in the Sun,” which resembles the band Nirvana, and their late songwriter, Kurt Cobain. They completed it by sourcing the music from “In Utero” and “Nevermind” (via Billboard). Creating the new song took similarities and writing tendencies.
The program works simply by listening to each part of the music and using deep learning programs to learn each artist’s unique styles. If you feed the program entire songs to listen to, you get a bunch of garbled and mixed sounds back at you. Still, if you take the time to feed each track in a song, it will learn the ins and outs of the artist to the point where it can make a brand-new song that will sound similar but not just repeat what it already heard.
15. AlphaFold is a deep-learning AI that enables medical breakthroughs.
Another one of Google’s creations, AlphaFold, is a program that assists researchers in predicting protein structures. In this case, proteins are molecules built from amino acids, and they are in every living cell of organisms and control cell functions. AlphaFold takes the data it creates and uses it to produce 3D simulations of these proteins (via Wired). Its most recent use was to help predict the protein structures of the SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. It works by studying the target’s genetic sequence and then creating a 3D layout of the proteins. Identifying the specific protein that the COVID-19 virus uses in rupturing the cell of its host as it replicated within the body led to its success. This knowledge could lead to further understanding of the virus and perhaps better and more efficient treatments.
AlphaFold also maintains a complete database of protein structures that anyone can access. For example, suppose you wanted to research the known protein structures for the ‘Canis lupus familiaris,’ otherwise known as the domesticated dog. In that case, you can access all that research, which is an astonishing 786 different types of proteins. An estimate shows that they discover over 30 million other proteins every year, and the current database holds information on over 200 million different kinds (via Wired).

14. EELY500 is allowing humans to inspect and repair underwater structures autonomously.
Created by Eelume, the goal for their robot Eely500 is to allow for completely autonomous operations underwater for months at a time (via GCE Ocean Technology). This application has several benefits. First of all, large and expensive ships carrying humans and equipment currently perform repairs and routine inspections. This not only contributes to water pollution but is also inefficient with costs. Furthermore, it saves time and money as there is no need for dangerous water diving or waiting for the weather to be good.
If Eely500 is successful, it will essentially live on the seafloor and conduct various operations without any human interaction (via GCE Ocean Technology). This can provide safety inspectors and engineers with real-time data regardless of wind or ocean conditions. It would enable faster repair time for many issues that can arise with underwater structures and substantially lower water pollution caused by large boats using current repair methods. Researchers have developed this robot to fit into very confined spaces. They have made it in the shape resembling an eel, making it so flexible that it can take on the form of a U, allowing it access to places that current methods and divers cannot get access to while underwater. It can have many sensors attached to its body and use its eight thrusters to get where it needs to go quickly.
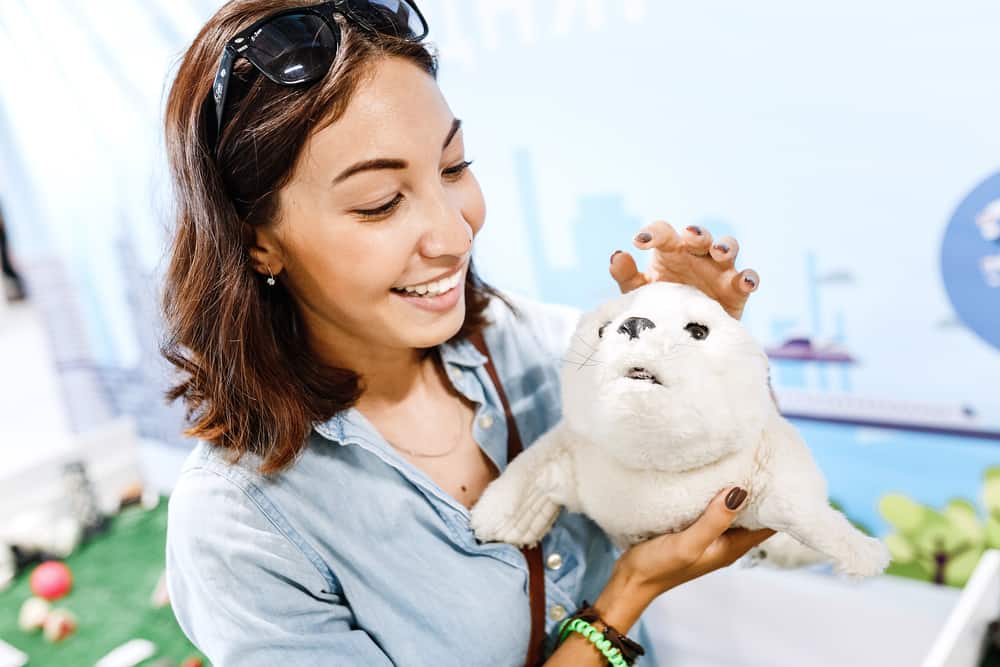

13. PARO is a baby seal robot using artificial intelligence to help with therapeutics.
This robotics endeavor is actually two fronts. The company behind the robot, AIST, developed it to support animals in therapy but without using real animals. Inventors designed PARO as if it was a real baby Harper seal, but it also has multiple sensors that allow it to interact with people (via PARO Robots). It has tactile sensors to “feel” being a pet and posture sensors to know when someone picks it up or moves it. Using its light sensor, it can tell whether it is daytime or nighttime and decide if it should be sleeping or not. Not only can it recognize your voice, but it can tell from where your voice is coming from and remember repeated words like names or greetings.
This level of AI has many positive results, such as increased interactions between patients and health providers and reducing stress for patients as well as their caretakers. The Guinness World Records certified this artificial intelligence as the World’s Most Therapeutic Robot. PARO has even met President Obama (via PARO Robots)!

12. Robots may no longer need electricity to operate.
Scientists and Engineers at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory have created what they are calling “water-walking” liquid robots (via News Center). Essentially, these tiny robots function like miniature submarines, capable of going underwater and retrieving substances and returning to the surface with them. However, the question always remained, how can they work for long periods without some form of power or electricity? They operate using chemicals instead of electricity, controlling their buoyancy to rise or sink in the water. As long as they have access to chemicals in the liquids they are kept in, they can function without end.
As it stands, they can perform specific tasks like detecting different kinds of gas. They also believe it may have applications in the medical fields by being a drug delivery system or screening chemical samples. Depending on their configuration, they can also perform multiple tasks at once, allowing for their use to be diverse but routine at the same time. The robots themselves are also tiny, typically looking like little open sacks and just barely measuring in at 2 millimeters in diameter (via News Center).

11. Artificial intelligence is getting better at navigating mazes and mimicking brains.
Using a robot kit made by Lego of all things, researchers at the Eindhoven University of Technology have been training AI robotics to learn how to navigate maze structures in the same way that mice learn how. In a mouse, its brain changes ever so slightly when it discovers a new thing, just like humans. In the robotics case, by adjusting the amount of electricity in the device, the robot can learn the correct way to escape the maze (via Science Daily).
Originally, they programmed the robot to turn only right within the maze. Whenever it came across a dead end or was otherwise unable to proceed, it was to return to the original path or then to try and turn left or go forward. Using this method, it escaped the 2×2-meter maze after 16 attempts as each attempt (via Science Daily). It would remember where the false turns were located and were able to avoid it.
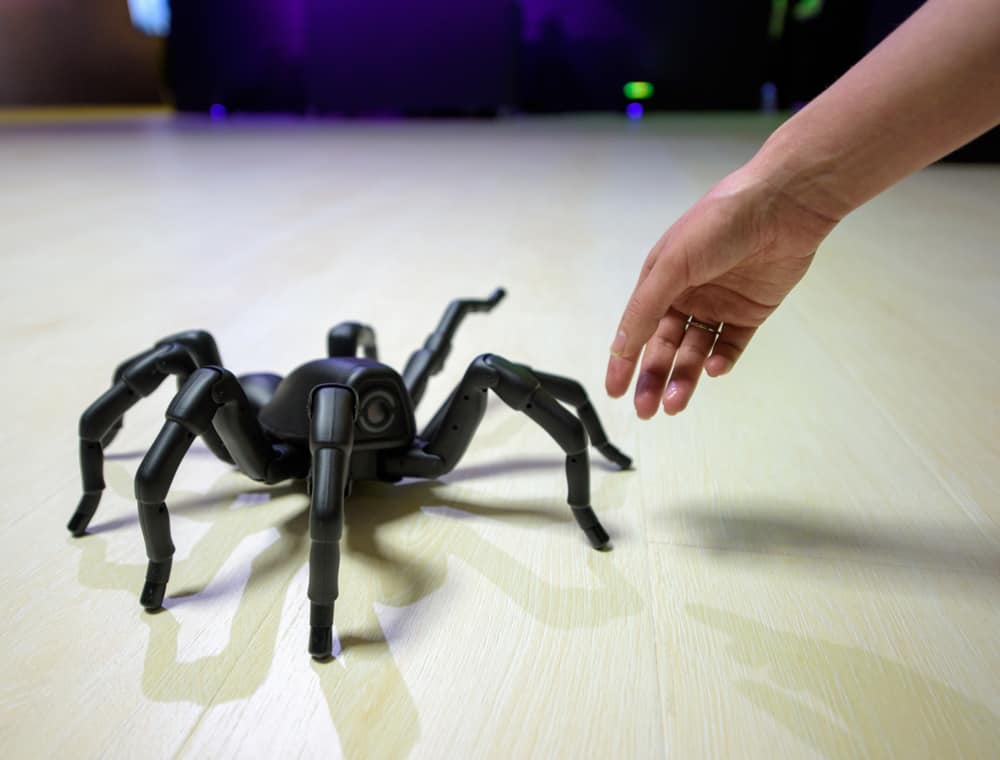

10. Swarming robots are here and learning quickly.
Yasemin Ozkan-Aydin is a robotics engineer and assistant professor of electrical engineering at the University of Notre Dame (via Science Daily). You can thank her for potentially creating swarms of spider-sized, multi-legged robots. She used 3D printing technology to make four robots (via Science Daily). They were about six to eight inches in size and had a microcontroller, a light sensor, and two magnetic touch sensors.
The purpose behind these creations was to study the ability of bees, ants, and other small creatures to solve problems and their behaviors collectively. So far, the robots have learned how to bridge gaps with their bodies, connect to each other to move objects that an individual would be unable to move, and help each other if one of the units gets stuck.
9. Deep learning artificial intelligence is making 3D X-rays possible.
Usually, taking an x-ray is a simple procedure, but adding a third dimension to the image makes for a much more mathematically intensive process. Even modern-day supercomputers take quite a bit of time to process. However, this is likely to change soon due to the Department of Energy and Argonne National Laboratory. They are working to create a neural network trained by artificial intelligence to generate images from simulations quickly. As the web gets better acquainted, it can better fill in any missing data to create a perfect 3D print (via Science Daily).
The technology of this caliber wouldn’t just be helpful if you broke your arm; it also will have significant applications in astronomy and any other area that relies on 3-dimensional data. After complete training, they estimate a network will be over 500 times quicker than current standard methods (via Science Daily).

8. Autonomous cars are learning how to drive without GPS.
Researchers and developers rely on new AI learning methods using old technology to accomplish this feat (via Science Daily). They use a visual terrain-relative navigation process, which researchers first created back in the ’60s. This system uses images in its database to navigate the vehicle; however, even things like weather or snow can disrupt it from identifying pictures correctly.
However, modern AI is giving the system quite a boost as it allows the program to remove obstacles and allows the program to see things it could not see before. The new AI will teach itself by looking for patterns in the images that a human eye would likely miss completely. Once it does this, up to 92% of attempts to recognize pictures were successful, unlike 50% without AI assistance (via Science Daily).

7. AI is making it easier to predict and treat strokes.
Strokes affect over 800,000 in the USA alone and over 5 million people around the globe, so it is crucial to develop prevention, recognition, and treatments (via AJRN). This is where artificial intelligence is proliferating. Using statistical analysis, AI routines can identify potential issues such as clogged arteries or hemorrhaging and predict outcomes for treatments at a much faster and far more accurate rate than a human mind is likely to.
Using a process called convolutional neural networking, researchers have already achieved par with human accuracy in having the AI identify common everyday objects such as dogs (via AJRN). This process is currently the most popular and successful image classification for medical purposes. They continue to train the AI, which shows advances in detecting diseases like colon cancers, pulmonary nodules, and other medical conditions.
6. The most advanced human-shaped robot.
What was once a pipe dream you will see in a sci-fi film now feels like it’s here, and soon it might be a reality. Engineered Arts created the world’s most advanced robot that looks and has facial movements just like a human. They made Ameca as a base for the perfect humanoid robot design that can interact with humans with its AI technology upgraded over time (via Engineered Arts). To complement the AI, they also designed a human-like artificial body for Ameca that is still being tested and developed. They are working to work alongside their Tritium robot operating system.
Ameca is a new tool to develop AI to a whole new level. However, you can also even purchase or rent it for events like conventions or have it as a visitor attraction (via Engineered Arts). It is used for companies to expand their horizons, research, and upgrade their systems for many uses, which will be broadened more in the future to work for more than just an attraction or an educational tool that can go beyond a laboratory. Since its system is so advanced, you can upgrade Ameca without buying a new robot to keep advancing.

5. There is an impressive stunt robot that can fly through the air and amaze people.
Disney Imagineers have been working for years to make the experience of visiting their parks as magical as possible. So, when they revealed the Avengers Campus, they went to work on one of the most technologically advanced animatronics they have ever made. They created the “Stuntronic” to wow guests. How? By making a robot that can fly through the air as a superhero would. In this case, Spider-Man (via Disney). Imageneers combine advanced robotics with dynamic movements that look like realistic aerial stunts made by a human. However, a humanoid robot actually drives it.
They programmed the Stuntronics figure to soar through the air like the web-slinger. It can do various twists, flips and poses that look like a human. The robot lands perfectly every time. Their first challenge was finding a way to control the landing with precision every single time so that every stunt looked perfect no matter how many times it had to do it. Scientists at their research lab worked on harnessing the law of conservation of angular momentum (via Disney). That way, it will be as realistic as it can be. They also created a platform to make other characters come to life with breathtaking aerial stunts that look like they came out of the comic book pages.
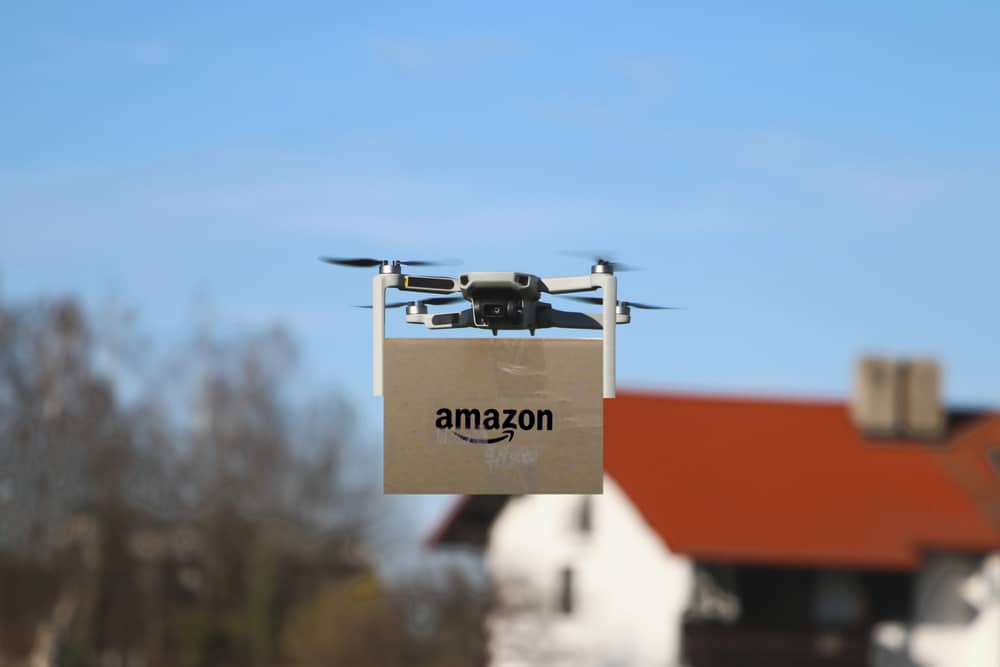

4. Amazon Air can get your order to you in 30 minutes or less (but the pizza isn’t free).
Amazon is currently in the works to bring the world its fastest delivery system yet. How? By utilizing small drones to deliver packages that weigh five pounds or less directly to your door. The benefits of a program such as this are enormous. There are no more bulky delivery trucks, no more time spent on the roads, safer delivery, and fewer packaging materials. Amazon is currently testing drones and other aerial vehicles for future use (via Amazon). The drones will need multiple sensors to traverse a wide array of obstacles, like buildings, power lines, and trees. Amazon states they are using “sophisticated ‘sense and avoid’ technology.”
The Alphabet subsidiary Wing has also tested home delivery services using drones (via Wing). So far, they have used drones to deliver over 10,000 cups of coffee, 1200 roasted chickens, and 1,000 loaves of bread to citizens of Logan, Australia. Lucky them! That is where it is currently conducting research and tests. In fact, the testing is going so well that Wing reports it hasn’t had a single problem with its delivery service during the trials. That counts thousands of flight and delivery tests simultaneously.
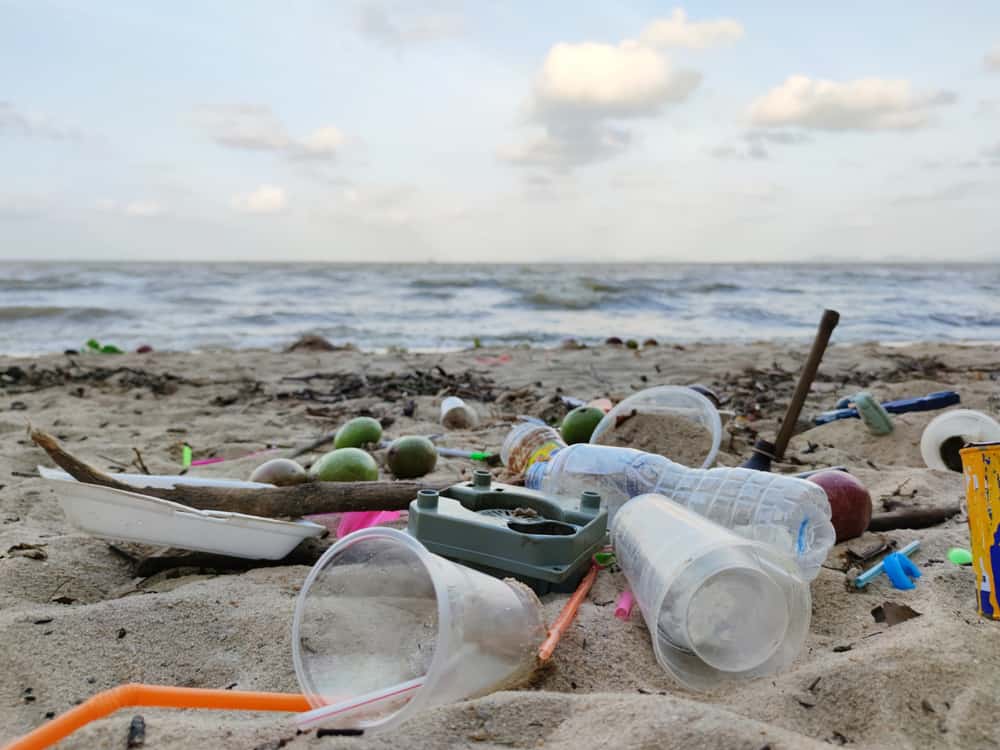

3. Robots are helping keep our beaches and ocean fronts clean.
One particular robot named Bebot is hanging around Florida beaches. Why? Because they are testing this AI’s abilities, of course! Its primary goal is to quickly clean the sand from trash and debris from humans. Created and operated by 4Oceans, it works simply by driving around the beach, sifting through the sand at up to 10 centimeters deep, and pulling out the trash it is programmed to look for. Currently, it can identify and clean cigarette butts, food wrappers, bottle caps, and plastic bits. It can also gather other bits of garbage up to 1 centimeter in size.
Bebot is also built to be eco-friendly, as it is solar-powered, remote-controlled, runs silently, and produces no harmful emissions. It can clean up to 3,000 square meters of sand every hour, making it over 20 times faster than human hands (via Screen Rant). It can also be remotely operated from nearly 1,000 feet away, making it easier not to disturb local animal populations. As of August 2021, this robotic cleaner has cleaned over 20 million pounds of trash from beaches (via Good News Network).

2. Robotic sports teams could be coming in the future.
During the 2020 Olympics, a unique spectacle happened during the United States vs. France men’s basketball game (via Screen Rant). During halftime, Toyota brought out their robot named Que. They demonstrated how artificial intelligence could flash basketballs from anywhere on the court. The robot stands at six feet, ten inches tall! It utilizes sensors in its chest and head to accurately sink a ball nearly 100% of the time.
There are some downsides to it, though, as Que cannot run, dribble or dunk the ball (via Screen Rant). It can also take 10 to 20 seconds to line up a shot and make it. Toyota’s robot’s point is not to sink basketballs but is part of a larger goal to teach a robot to be as smart as possible. It is part of a 1 billion dollar investment to bring new ways of autonomy into vehicles and robots. They can use the data from Que making shots to learn how robotics deals with distance and force to make cars safer and more efficient.

1. Magnets improve the mobility of prosthetic limbs.
Finding ways to make prosthetics feel as natural as possible has been a challenge for many decades. Finally, a group of researchers is now developing a way to provide a much more precise movement and control of prosthetic limbs. MIT’s Media Lab scientists found that inserting a small magnetic bead in the muscle tissue within the amputated residuum can perfectly measure how a muscle contract (via MIT)via MIT). It sends a message to the brain and the bionic prosthetic to contract in just milliseconds. Researchers call it magnetmicrometry (MM). They hope to replace electromyography for a better link to the peripheral nervous system to bionic limbs.
The procedure is also less invasive with a low regulatory hurdle, making it a cheaper alternative. People with low mobility due to accidents can also use the technology (via MIT). How? It provides a new way to send a signal from the injured muscle to the neurological system to a bionic exoskeleton. As a result, it can help the person walk with no problems. It can also work for rehabilitation after a nerve or spinal cord injury to stimulate muscle movement and bring better control of the body. This method provides an easier way to help patients have an everyday life with less hassle.

