We all have both a mother and father that gave us life. Whether they remain by our side as we grow up might be up in the air, but we know they are at least responsible for the life we live today. Each parent brings their own genetics into things, and we are born with a combination of their DNA. Generations of people are born with this combo DNA, taking on many of the same traits their parents have. However, sometimes mutations happen that differ us from our ancestors. This causes rare genetic traits, some of which we pass on to our children.
While possessing one of these rare genetic traits might not be noticeable for most, there are some that are. For example, some people are able to make their tongue into a three-leaf clover. This is a form of rolling the tongue, but specialized. Nearly 84% of people can roll their tongue but only 14.7% of people can do a three-leaf clover without assistance. It is one of the rare genetic traits that actually pass down from parent to child. Of course, some are first-generation and pass it down to their kids later. There are many traits like this as well as others that are even more incredible, let’s dive into them now!

Curly Hair
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: Roughly 11%
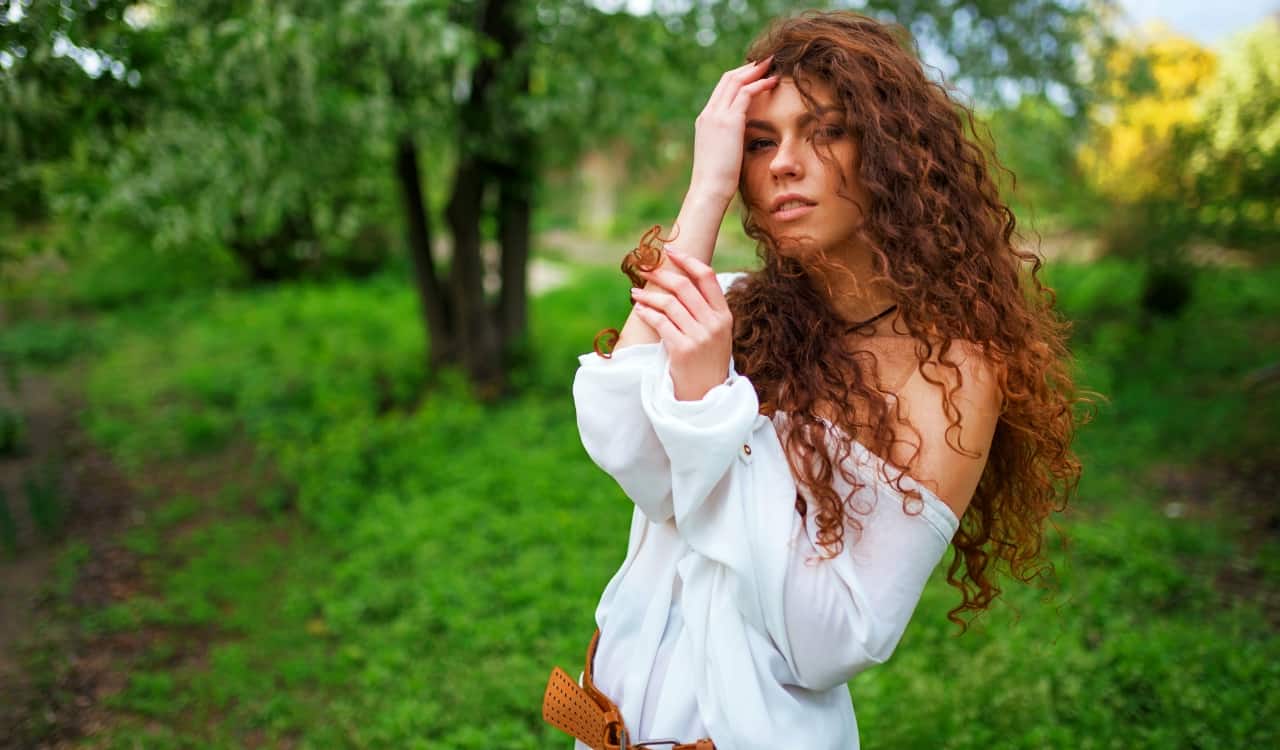
Curly hair is something a lot of people love, and actually have to fake. They might do this with a curling iron, but the curls they add are small and picked out to fit a specific look. For those with truly curly hair, having the chance to “pick” where their curls show up is nonexistent. It is a great look, but very few people have naturally curly hair. We do not mean small curls when we state this, by the way.

For example, if you do not brush your hair well and have a few curls at the bottom or if your bangs get so long they curl up. We mean people who have most sections of their hair curl on them naturally. These people are pretty rare, funny enough. Curly hair is one of the world’s rare genetic traits because only 11% of the world’s population has it. In fact, there are some people who have siblings with curly hair while they do not, showing just how rare it can be even in the same immediate family.

Natural Blonde Hair
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: Between 2 to 6%
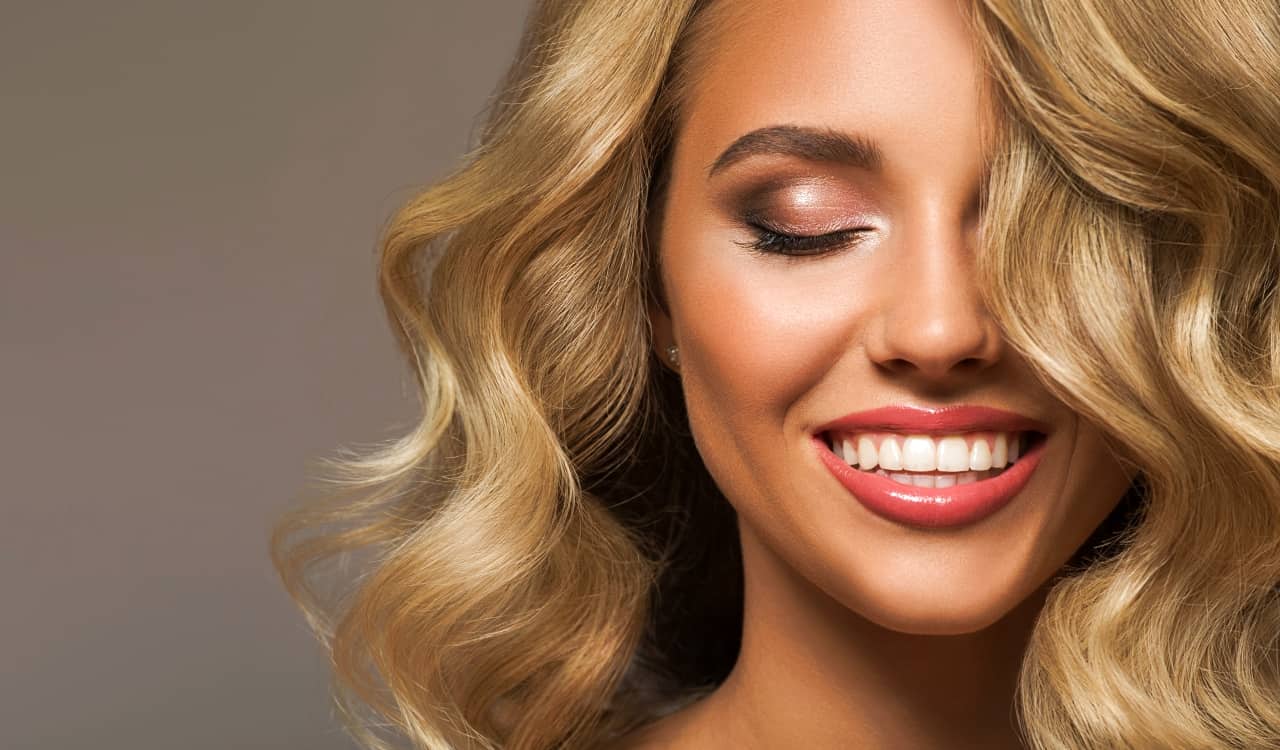
We should make sure to reference here that when we state “natural blonde hair,” we mean those that are only blonde. Not those that have brown or black within the hair, aka “dirty blonde” hair. It is widely assumed we have more blonde people in the world than we actually do. “Blonde” is one of the most popular hair colors that people dye their hair to fit. It is stated that three in four caucasian women dye their hair blonde. This is why there are significantly more “bottle blondes” than natural blondes.

Moreover, natural blonde hair is more common for children than adults. This is due to the fact that hair tends to darken as we age, causing more adults to end up with brown or black hair before going grey or white. It is tough to get a true percentage of adults with this natural color, again due to the mass popularity of dying hair. However, due to the help of hairdressers and truthful people, it has been determined between 2 to 6% of adults have naturally blonde hair in the world today.
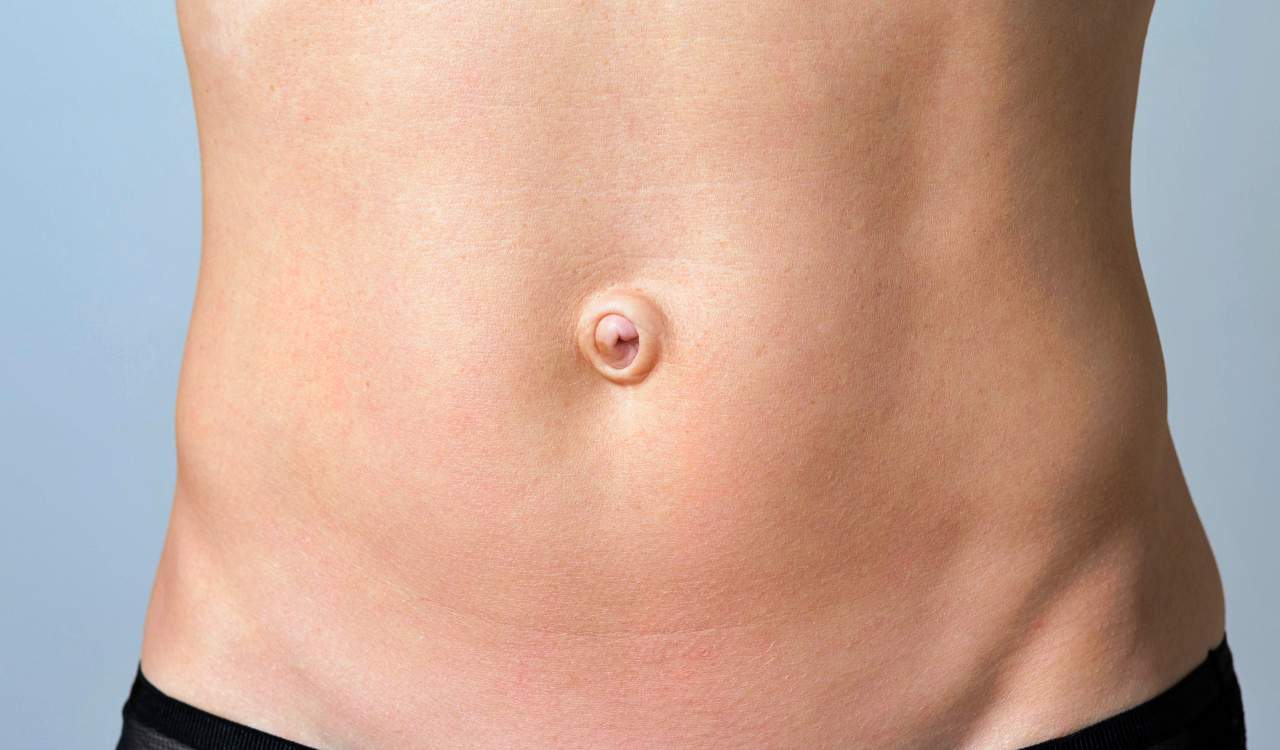
Inverted Navel
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: 10%
Rare genetic traits like an inverted navel can be really odd to see among adults. However, they are not exactly crazy to see among young children. Children that are newborns all the way up to a few years old may have what is commonly called an “outie belly button.” Of course, the true name for this is an inverted navel, but most people do not know the true medical term for it. Most children who have an inverted naval will eventually see it sink in to look normal.

Although, it can last for others into their teenage years. It does usually go away before that timeframe, but the cases change often depending on the size of the person. While some believe that the naval being inverted or not is determined by how the umbilical cord is cut, this is not the case. How the scar heals there afterward is really the biggest factor. Sometimes, the child might even have a small hernia at birth that causes it too. Today, only 10% of adults have any form of inverted naval.

The DEC2 Gene
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: Around 3%
The DEC2 gene is one of the rare genetic traits that many wish they had. People with the DEC2 gene do not need to sleep as much as a normal person to function at their body’s maximum capacity. Most people need around 8 hours of proper sleep per night for them to function properly. Sleep is important for the function of our brain and it also helps our bodies heal from numerous issues. Doctors might recommend sleep for people with a cold or flu due to this.

Often called the “no sleep” gene, that is actually a common mistake. People with DEC2 need sleep, but only 4 to 6 hours at the most. Some might say “well I sleep that much so I might have it.” That is not always true. Some people have bad sleep patterns that cause a lack of sleep to occur. Yet these people need more sleep whereas those with DEC2 simply go through their full natural sleep cycle in less time than most. Therefore, they do not need the extra hours others do.
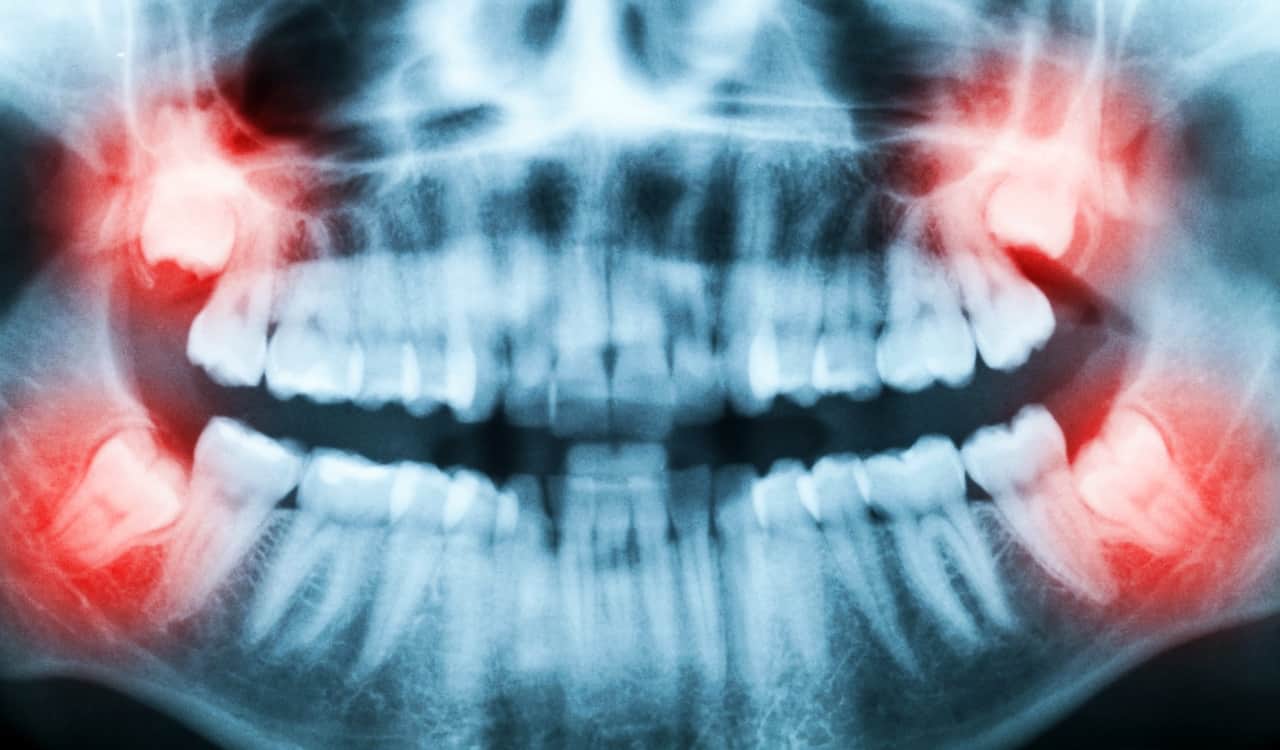
Born Without Wisdom Teeth
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: Around 20%
Most people end up having their wisdom teeth removed before they reach adulthood. Of course, some of these people did not need to remove them. Others were told to do so for the health of their teeth. When they come in, wisdom teeth will grow and push on the rest of your teeth. This can cause pain and even make your teeth crooked at times. Yet people went thousands of years without this problem, what happened? Funny enough, some people are born without them.
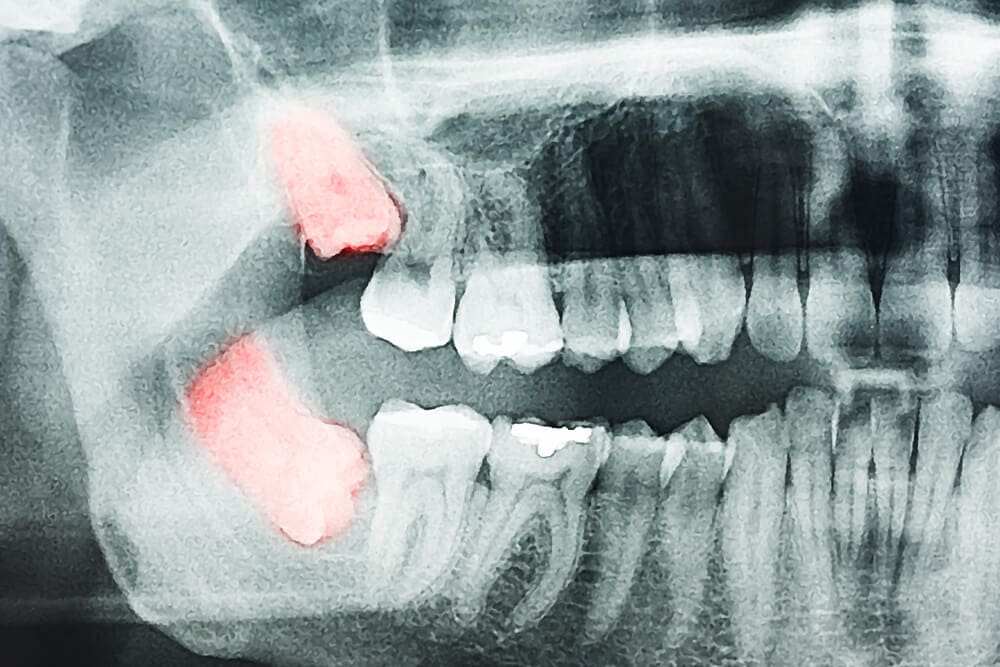
Nearly 100% of all indigenous Mexicans do not have wisdom teeth from birth. Yet nearly all Tasmanian Aborigines do. This presents a situation in which evolution dictated need, causing people in different parts of the world to need or not need wisdom teeth. Due to this, roughly 20% of the planet is now born without wisdom teeth. This used to be rarer than it is today but the percentage is climbing, meaning more will be born without them as we go into the future.

Photic Sneeze Reflex
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: 11 to 35%
One of the world’s rare genetic traits that can be quite annoying for people, the photic sneeze reflex is a condition where light causes someone to sneeze. We do not mean random light, such as one in your kitchen or the light from your television. It is usually only triggered by looking at very bright lights and other various stimuli. The reflex affects everyone who has it differently. Some can handle brighter lights than others, for example. It actually has a more official name, which is quite funny.

That name is Autosomal Dominant Compelling Helio-Ophthalmic Outburst. This is abbreviated as literally ACHOO. We know, we know. Of course, others with a lesser sense of humor also refer to it as “photosneezia.” It’s hard to get an accurate number of people affected by the trait. This is why a wide range of 11 to 35% of the world is said to have it. However, according to the Journal of the American Optometric Association, the majority of those affected by it are actually white females.
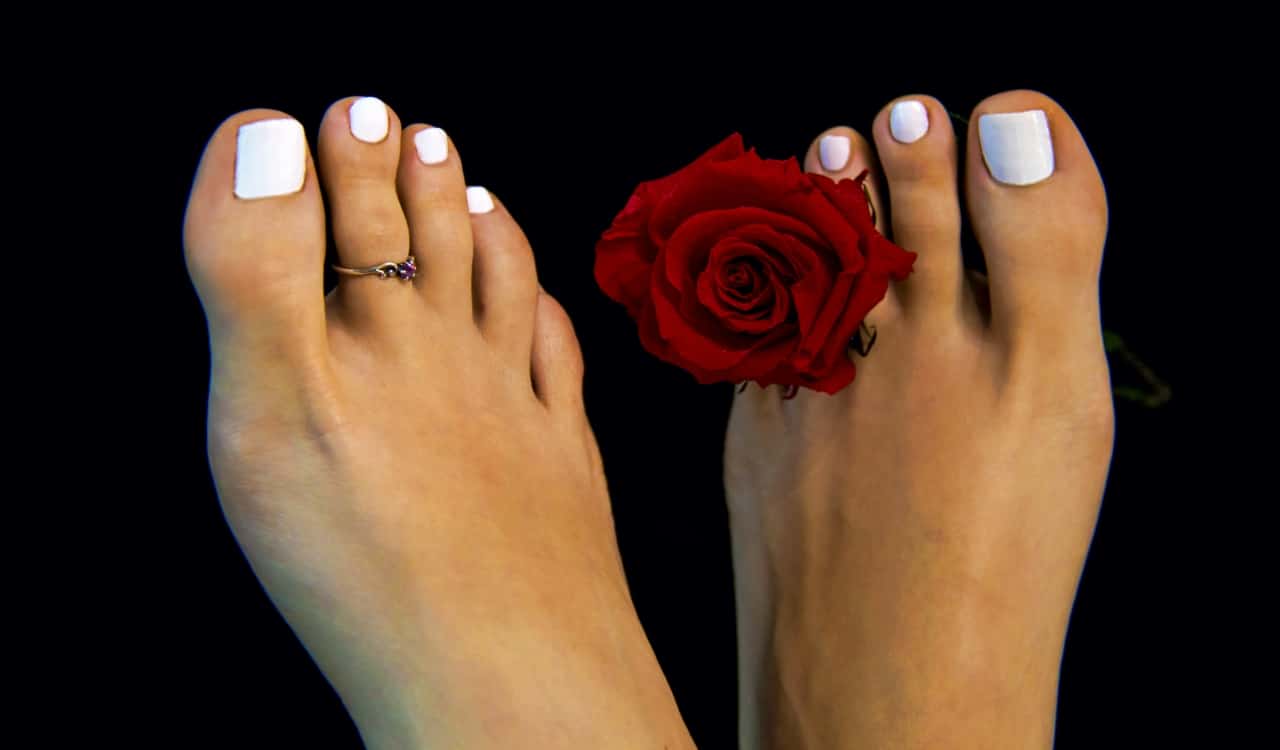
Morton’s Toe
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: Roughly 10%
Morton’s Toe is quite often something that looks weird to everyone who sees it. Most people have five toes on each foot, with the literal “big toe” on both feet. Of course, it is located on the far right of a person’s right foot, while on the far left of a person’s left foot. For most people, the “big toe” is referred to as such because it is the biggest toe on the foot. But for those with Morton’s Toe, that is not the case.
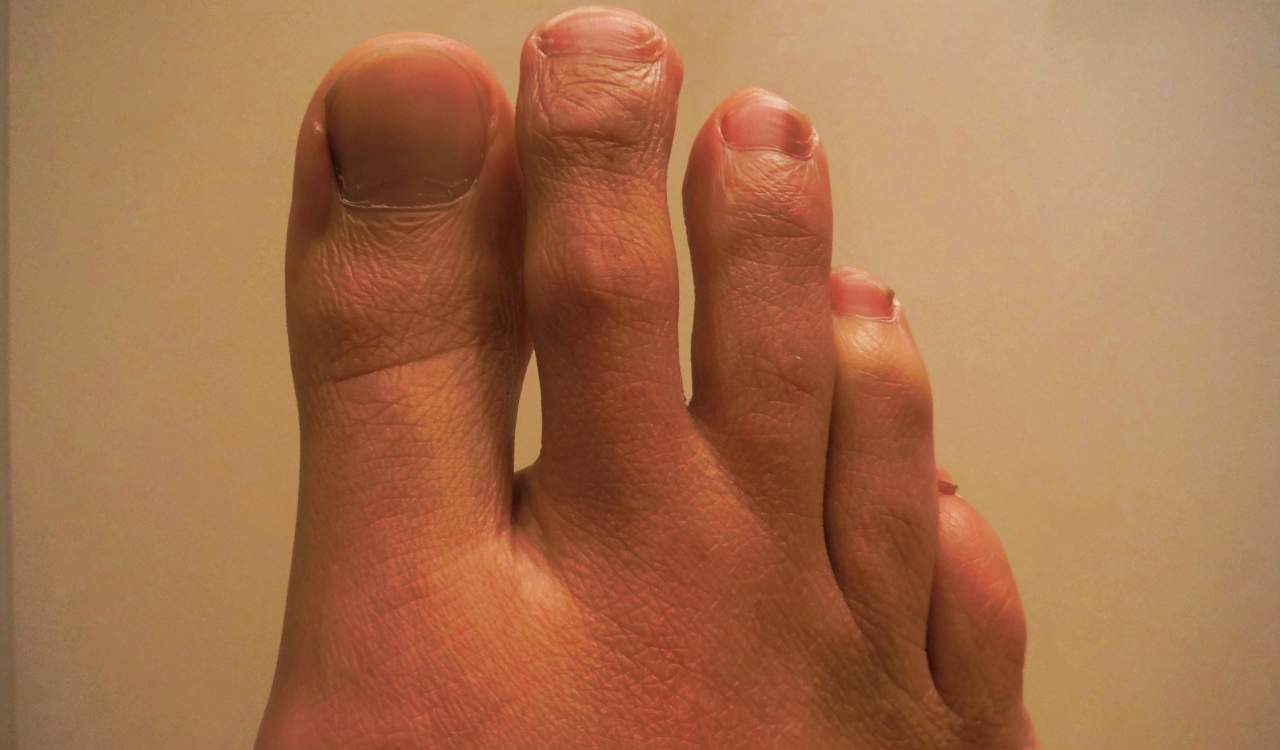
For those people, the “big toe” is actually smaller than their second toe. The look of those with this genetic trait often varies among those with it. For some, it is the same height as their big toe but not as wide. For others, it is just as wide as the big toe. Meanwhile, for others, it is just as tall and wide as the big toe. You might get some who see the second toe grow taller or wider than the big toe as well. Interestingly, the Statue of Liberty in New York actually has the Morton’s Toe genetic trait too.
X-Lines On Hands
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: 3%
Everyone has lines on their hands, but the way those lines look will vary widely among literally everyone. Yet for some, the way their lines look will be very different. For some, there is a rare phenomenon where the letter “X” will be formed on BOTH hands. The writer of this very article actually has this exact genetic trait. For the ancient Egyptians and Greeks, there were many meanings behind the “X-Hands.” They used to believe it was a sign of strong character or that a person was destined for greatness.

Of course, “palmistry,” or the foretelling of the future using a person’s palms, is complete garbage. It means nothing to have an “X” on your hands. However, it is still one of the world’s rare genetic traits as only 3% of the human population has this. This might differ a bit among our primate friends such as chimps or great apes. To be fair, it made sense to think the “X” meant something as Alexander the Great among other leaders in history had this “X” letter on both hands. Therefore, there “might” be something to it.
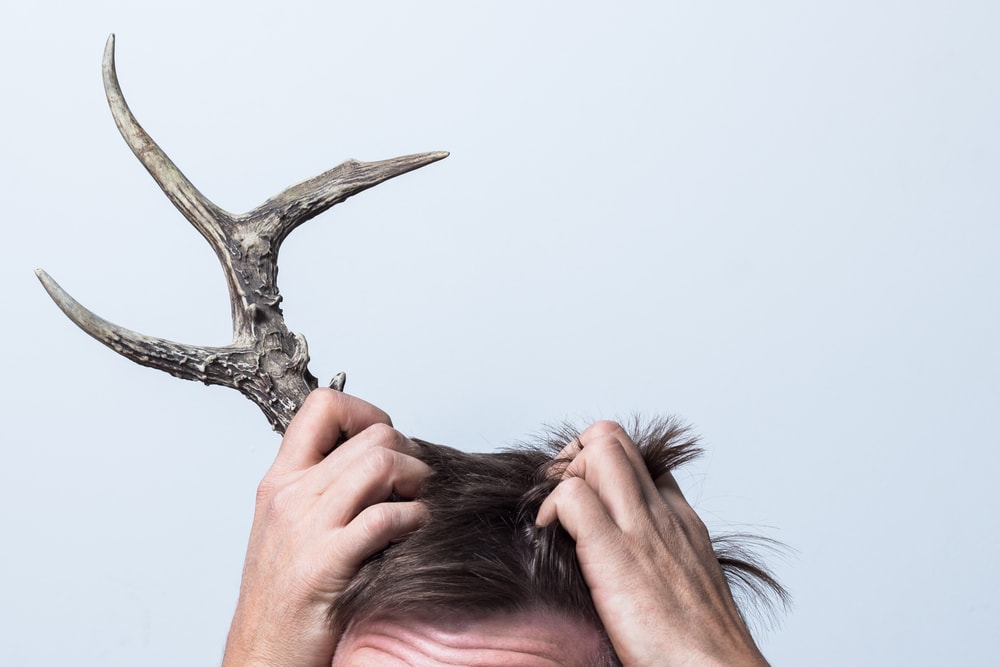

Cutaneous Horn
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: Less Than 10%
People who have cutaneous horns were often referred to as devils due to religious groups not grasping scientific phenomenons. This specific condition has been around for centuries, and religious types pounced whenever they saw someone with one or more horns on their body. Referred to as cutaneous horns or cornu cutaneum, the horn or horns a person gets are simply unusual skin tumors.
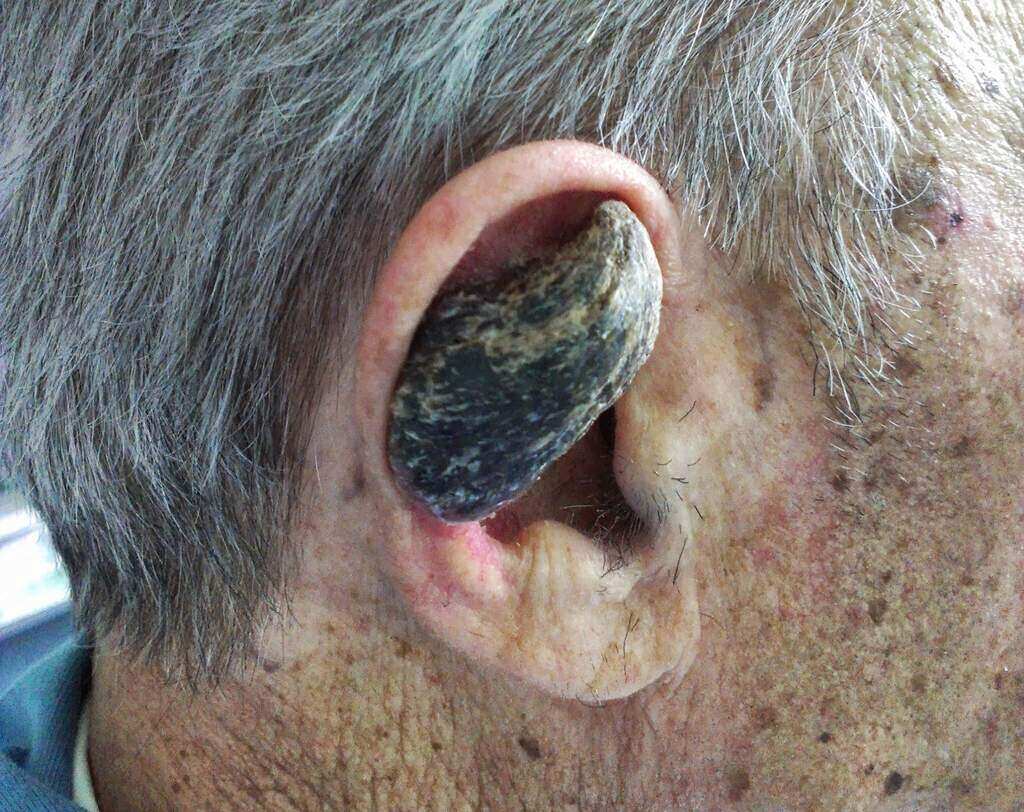
Basically, these horns can appear pretty much anywhere on a person’s body. They often are seen on the head or face. But they can also come out of the arms or legs too. While most of the horns can be relatively small, there are rare cases where they grow very large. A French woman named Madame Dimanche had a horn that measured out to 10 inches! The good thing is that these horns can be removed today. The way it is done will differ depending on size and how cancerous it is or is not.
HIV Resistance Mutation
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: Around 1%
HIV/AIDS might not be as much of a death sentence as it used to be. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) itself causes immune system problems. This can cause someone to have trouble fighting off infections or viruses that others might be able to combat just fine. If it is not treated properly, HIV can turn into Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS). Due to the rise of scientific breakthroughs in this field, we are able to keep many people from ever ending up with AIDS if HIV is caught early enough. HIV can pass from person to person via a person’s main bodily fluids, such as their blood or sperm.
Although, women can pass it to men by the man being inside them at all. Sweat and spit, however, will not transfer it. Some have nothing to worry about though, as they are completely resistant to HIV. Those people have a rare genetic mutation called CCR5 Delta 32. The mutation caused the CCR5 co-receptor to be far smaller than normal, making it difficult for the HIV virus to enter cells. The main receptor is closed, preventing the virus from ever taking hold of a person’s body. Today, scientists are trying to mimic this via stem cells using cells from HIV-immune individuals. Making these people incredibly important.
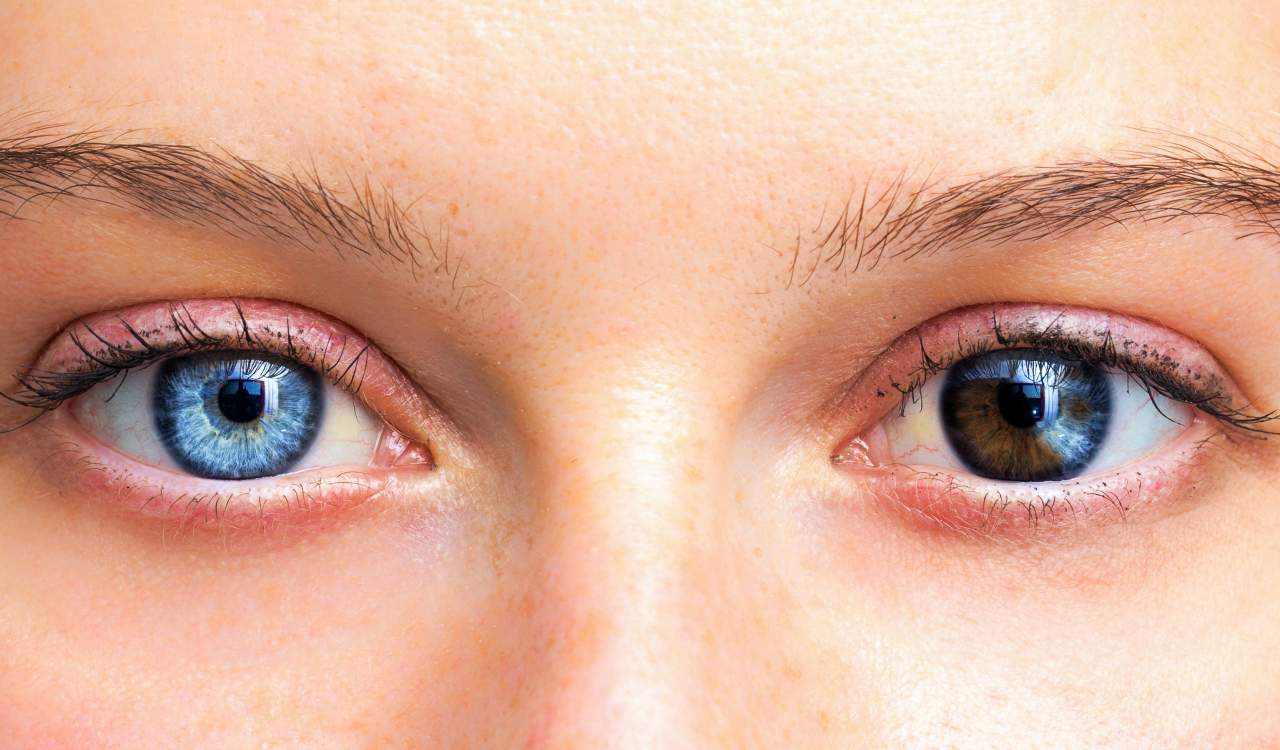

Heterochromia
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: 1%
Heterochromia is one of the rare genetic traits a lot of people know about by now. The reason for this is likely due to how obvious it is that a person has it. This is a genetic trait that causes a person to have two different colored eyes. However, those with different colored sections in each eye are also said to have this. In rare cases, a person with this trait might also see a difference in color for other body parts too. This can be a difference in skin color, hair, etc.
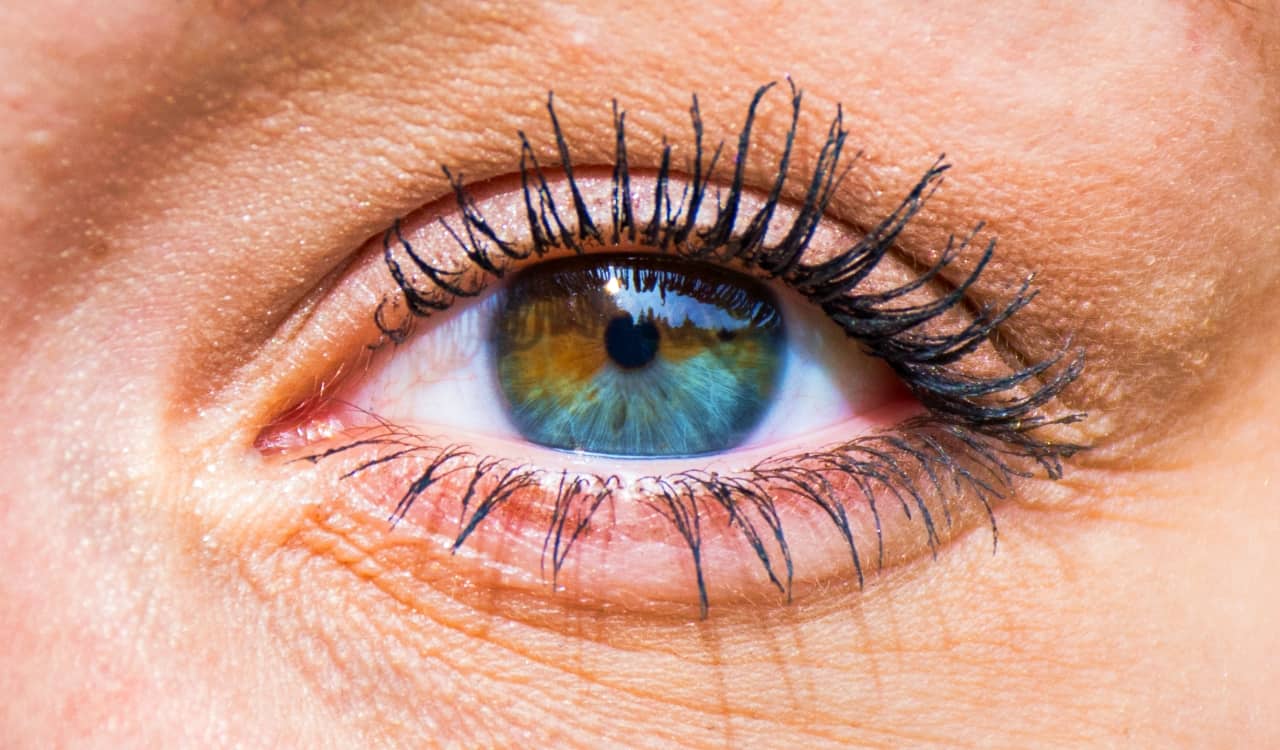
All of this comes down to how the genetic mutation works. Our eye color is affected by the melanin in our body. Heterochromia is the result of a mutation that led to an error in the distribution of melanin before a person was born. Of course, the most dramatic and obvious heterochromia cases are those with broadly different eye colors, specifically in the iris. It can be really wild to see but often beautiful. Interestingly, only 1% of the world’s population has any version of heterochromia.
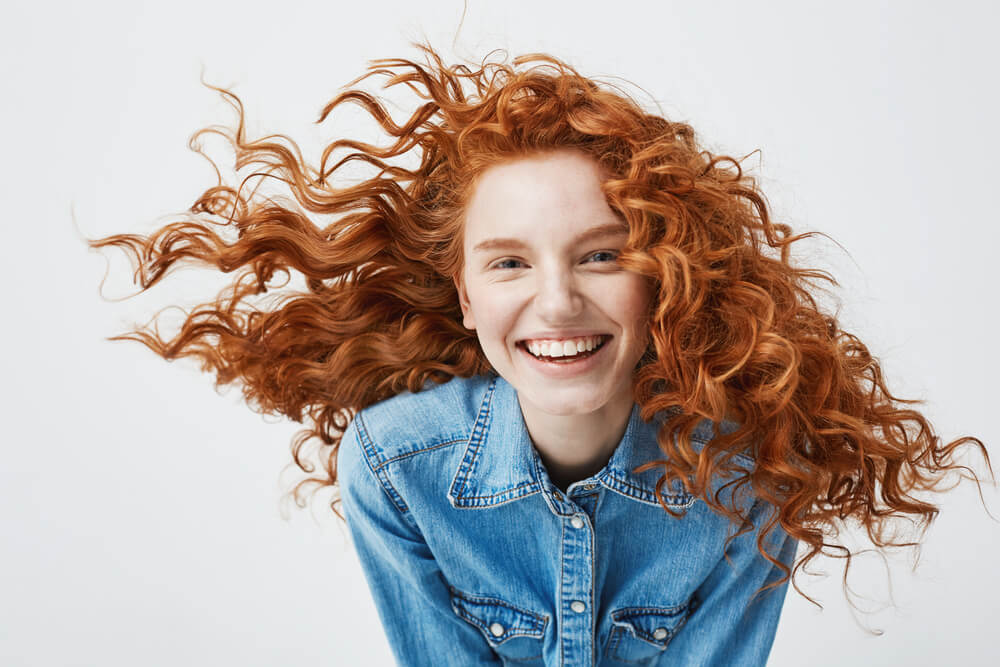

Red Hair
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: 1 to 2%
If you thought having naturally blonde hair as an adult seemed rare, having red hair is even rarer. Many assume most people from Ireland have red hair, or at least several in the United Kingdom. However, the most common hair color there (as it is worldwide) is brown or black. In fact, you’ll find more people with brown hair in Ireland than red hair. While some assume if your mother or father has red hair, you will too, this is not always the case.

People can have redheads in the family but still not end up with this color. However, if one does have red hair, it is always due to genetics. Red hair comes from a mutation in the melanocortin 1 receptor or MC1R, which is usually passed down from parent to child. Essentially, this causes the body’s skin and hair cells to produce more than one specific type of melanin, as well as less of another. In some cases, the mutation does not affect a child but will still be passed on to their future child.
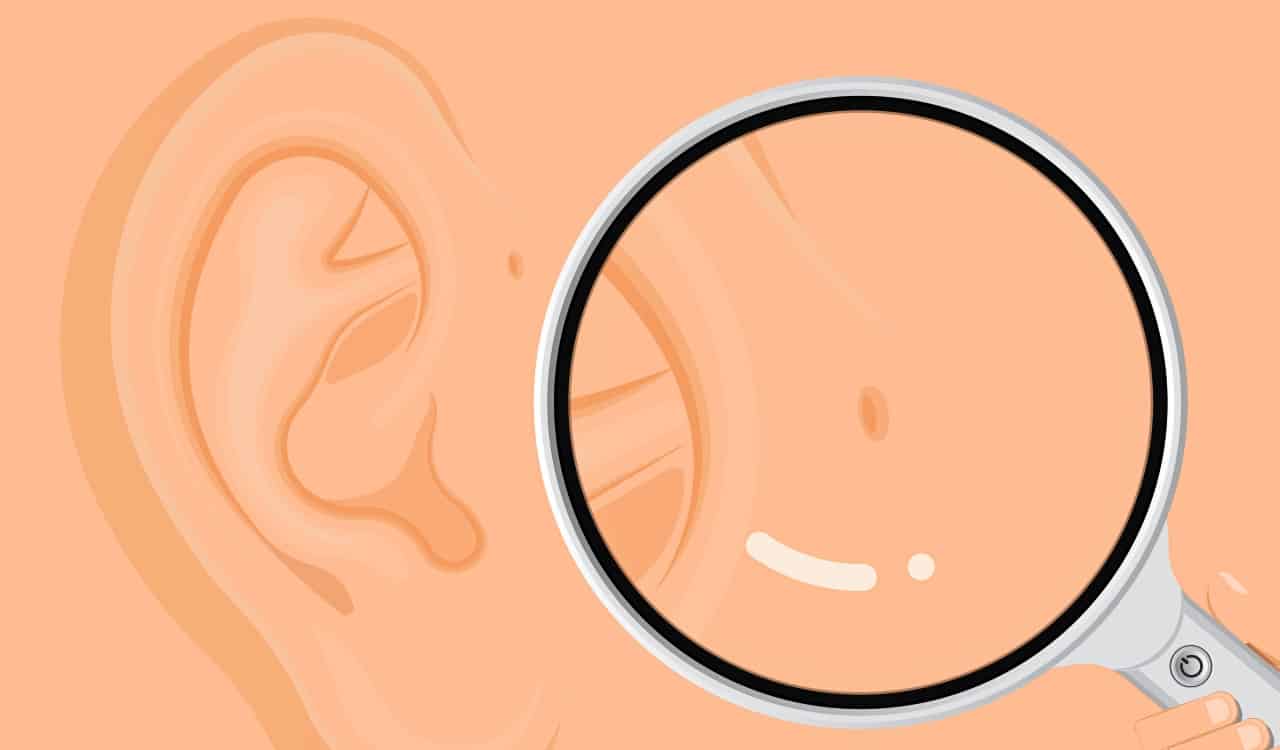

Preauricular Sinus
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: 1 to 10% (based on location)
When you talk about rare genetic traits that most people had no idea about, a preauricular sinus is likely on the top of that list for people. This is a condition that causes a small hole or dimple to develop on the outer ear. It’ll usually be found at the top of the ear where it connects to the side of the head. For most, it can look like the person had their ear pierced. For others, it can look very different.
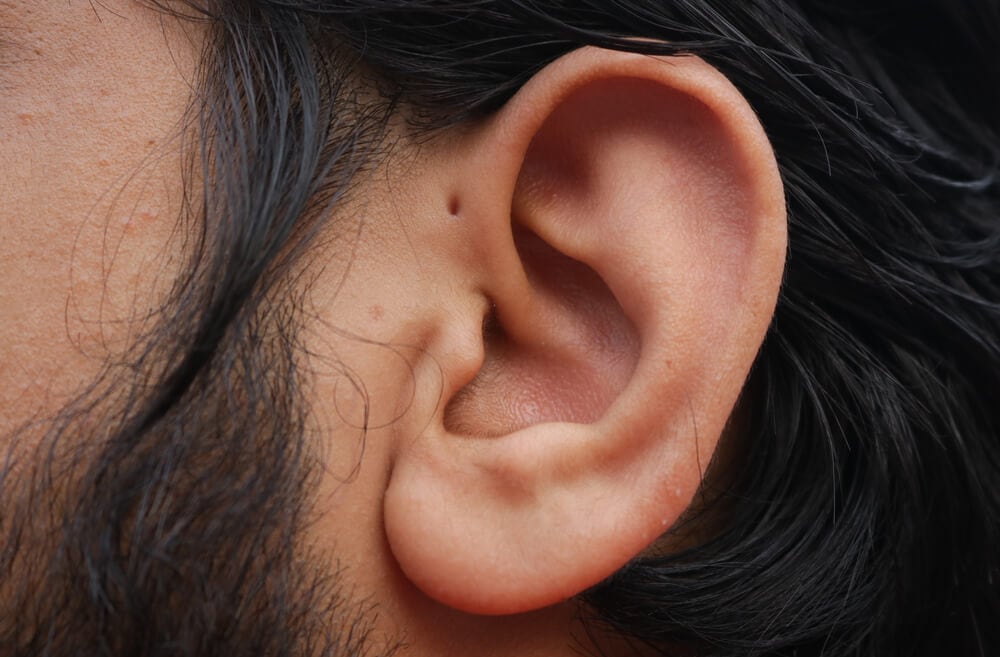
Of course, most of the time this is merely a hole in the ear and completely harmless. However, this is still a hole in the ear and that can open a person up for infection a bit more than the average person. The reason you’ve likely never heard of this is probably due to it being incredibly uncommon in the far West as well as most of Europe. Only 1% of people there have it. But in Asia and Africa, roughly 4 to 10% of people have this genetic trait.
Marfan Syndrome
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: Just Under 20%
Marfan Syndrome can be hard to deal with but it does offer incredible flexibility. This is one of those rare genetic traits that most parents do not want to pass on to their children. The syndrome affects a person’s body tissue where they will be tall and lanky but also have elongated limbs. While being tall and lanky is not so much an issue, the trouble with something like this is what happens on the inside of the body. A person’s heart, eyes, blood vessels, and overall skeleton can be impacted.

For many, their bones will dislocate easily without any major stress to force them to do so. The syndrome also causes extra strain on a person’s aorta and will usually always cause early-onset arthritis. There are some who have a less impactful version of the condition where their ligaments grow long and stretchy to offer hypermobility, but they are otherwise healthy. It is actually a bit more common than some might assume, as 1 in 5,000 people are born with the genetic mutation today.
Deficiency In PCSK9
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: Around 2%
While ever wishing to have a major deficiency in normal parts of the body would be a bad thing, it might not be in some specific situations. When it comes to rare genetic traits, one might love to have a deficiency in their Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 gene. Otherwise known as the PCSK9 gene, some people are born with a much smaller amount of this gene than the rest of us.
Having this deficiency can be a blessing in disguise, as it allows a person to have a reduced risk of heart disease by up to as much as 90 percent! On top of this, they do not have to worry about their cholesterol numbers like others. However, this deficiency does come with some drawbacks. The deficiency allows one to have an increased number of cholesterol esters, but this will impact glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. That will cause hyperglycemia and even impaired glucose tolerance.
Unbreakable Bones
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: Less Than 5%
When we state “unbreakable bones,” we want to make sure to reference that it is possible for anyone to break a bone. Yet there is a condition that simply makes it nearly impossible for certain people to do so. While it might not be one of the most well-known rare genetic traits, it is starting to rise in popularity. Called the LRP5 mutation, those affected by this will regulate and produce proteins that lead to a rise in bone density. The genetic mutation was relatively unknown until a car crash happened in 1994.
A man was involved in what was said to be an incredibly serious car accident but he did not break or even fracture a single bone. Researchers looked into this person further and eventually found that he had family members who also had strong skeletons. One family member actually underwent several failed hip replacements because surgeons could not screw into their bone. Further testing of the family members found that their bones were eight times as dense as the average person’s. This made their bones nearly impossible to break, at least under a normal situation.

Albinism
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: Around 6%
While some might say this is a questionable addition to our list of rare genetic traits, it actually counts a lot. Those with albinism are able to pass on this exact condition to their offspring. Of course, this is not always the case and a person can avoid albinism completely. It is obviously a lot easier to get if a person has two albino parents versus one. There are also two forms of albinism, Oculocutaneous (OCA) and Ocular Albinism (OA). Both have an effect on hair, skin, and eye pigmentation.

OCA mostly affects skin pigmentation but OA mostly affects a person’s eyes. But both could have normal looks for hair, eyes, or skin depending on the one you get. The National Organization for Albinism and Hypopigmentation claims skin and hair for people with OA might appear similar or only slightly lighter than other family members. Albinism overall is rare but OA is the rarest form of the condition, and can also cause several eye-related problems. Roughly 1 in 20,000 are albino today.

Left-Handedness
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: 15%
Some people claim that left-handedness has nothing to do with genetics, but this is highly untrue. If you have a left-handed parent, there is a solid chance you or a sibling will be left-handed. If you have two parents that are lefties, it is almost certainly their offspring(s) will be too. Although this has been studied for hundreds of years, we are just now coming to the conclusion that there is a biological, genetic cause for people being left-handed.
Some felt that hand preference was caused psychologically by the parent, but this was proven to be untrue. We now know two alleles are the cause of hand preference. Scientists found that the D-Gene and C-Gene, the two alleles, were responsible for everything. Those born with the D-Gene end up right-handed a majority of the time. Those born with the C-Gene, far less common, will have a random hand preference. This allows them to literally pick their left in a 50/50 split.
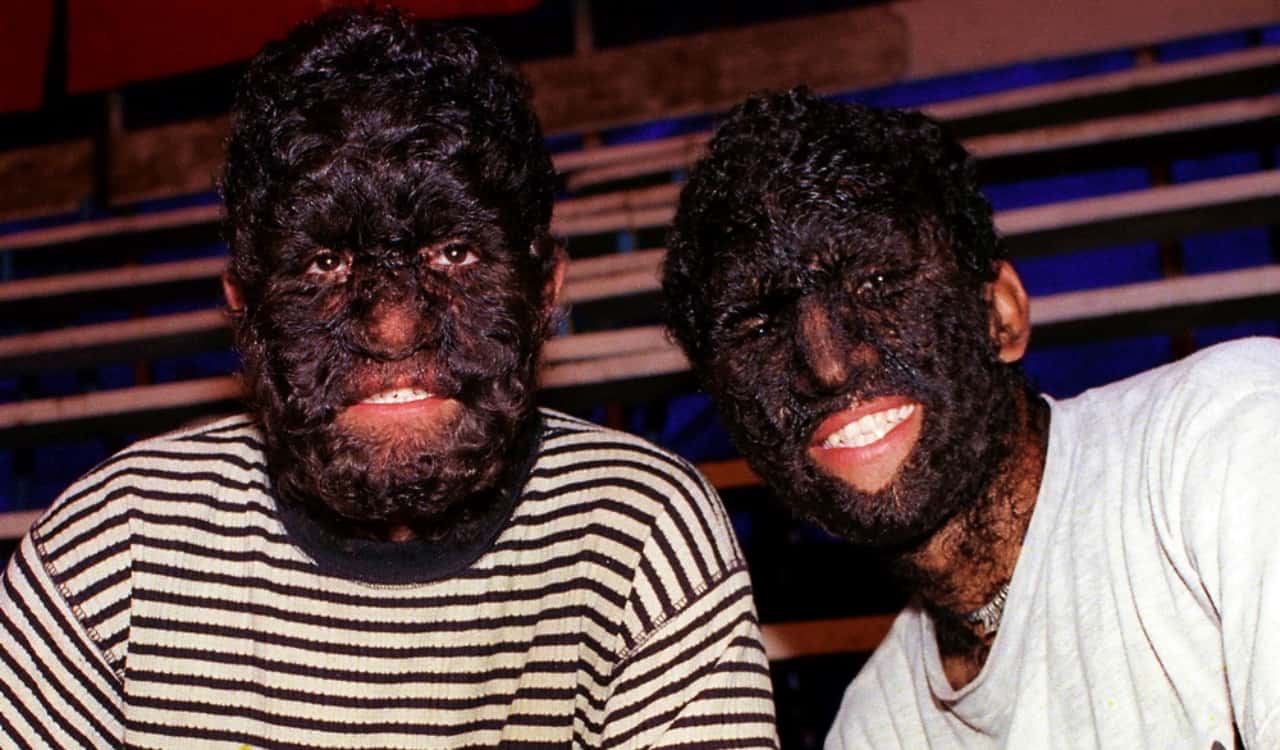

Ambras Syndrome
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: Less Than 1%
Ambras Syndrome is often referred to as the “werewolf disease.” The more scientific name for this is hypertrichosis, however. Those who have it will be completely covered in hair all over their bodies, regardless of gender/sex. For some, it might be isolated to certain areas of the body but most will be covered entirely. Those who have Ambras will not just be covered in a little hair. Rather, it is usually long, thick hair that can make one resemble our ancestors, the great ape. It rose to notoriety during the Middle Ages, mostly in Europe. Only 50 people were said to have had it since then.
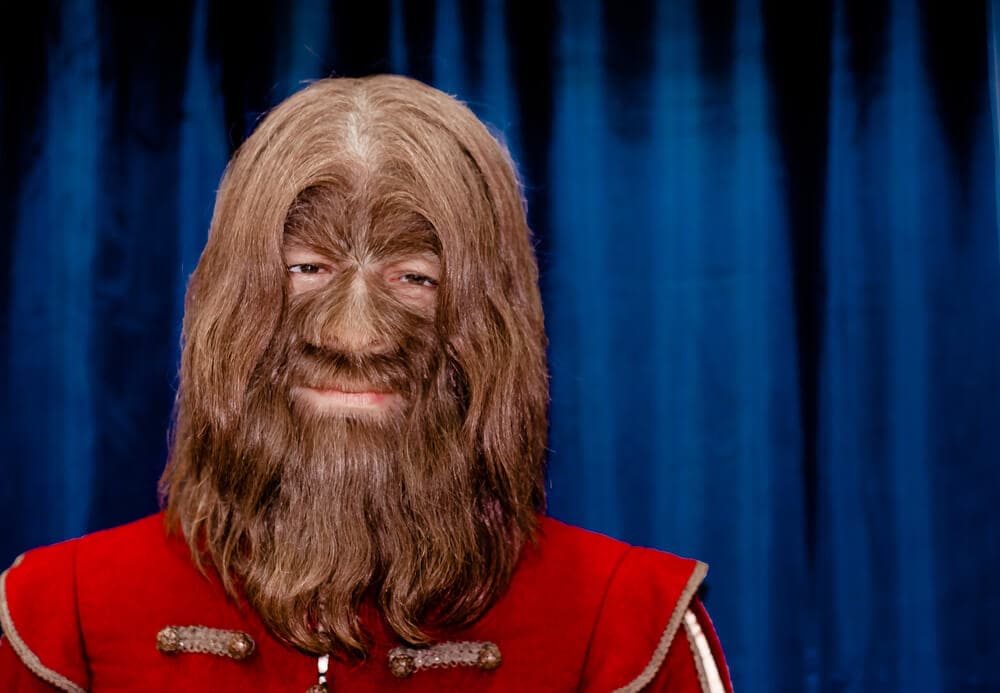

However, a relatively large family was eventually uncovered that had been living away from civilization for decades in an attempt to avoid issues with the public. It is now estimated several more could exist but might be hiding out. The gene responsible for this condition is called “TRPS1.” This gene causes a disruption in messages sent to cells regarding the development of follicles, which then results in the excessive hair growth Ambras Syndrome causes. Treatment now exists for people affected. This is almost always genetic, but there are some medical conditions or medicines that cause it too.
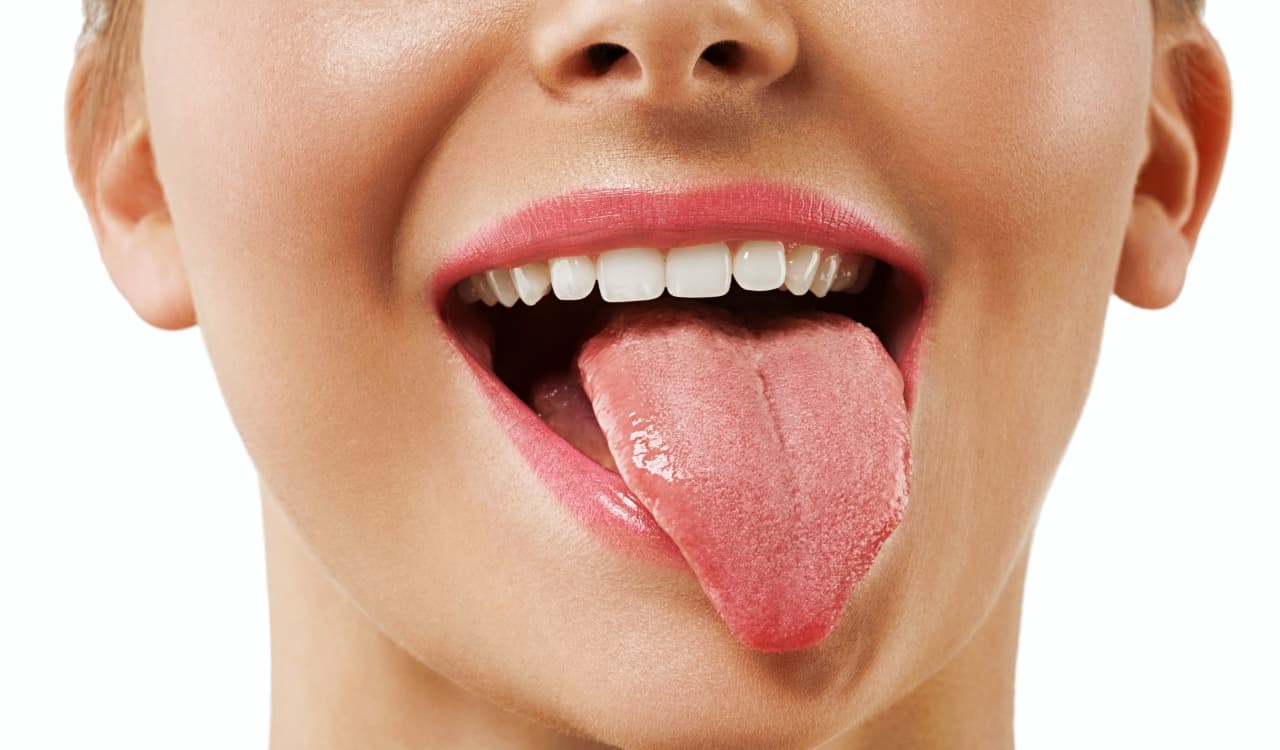

Superhuman Taste Buds
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: Roughly 25%
Rare genetic traits like superhuman taste buds might seem odd. However, those with this ability are able to accurately taste pretty much anything added to what they consume. How are they able to become superheroes in the culinary field? They are born with more visible taste papillae. These are those tiny dots everyone has on their tongue. Everyone has some visible versions of these dots, but these people have them in abundance.
This is useful but also problematic. Those with this tasting ability are more sensitive to foods, meaning that won’t be able to handle something that is very bitter, sweet, or salty. On top of this, they have more pain receptors on their tongue which makes them dislike spicy foods. Many who have superhuman taste buds do not like vegetables due to their bitter taste but they are not usually out of shape. This is due to the fact that they also do not like to consume a lot of sweet or fatty foods.
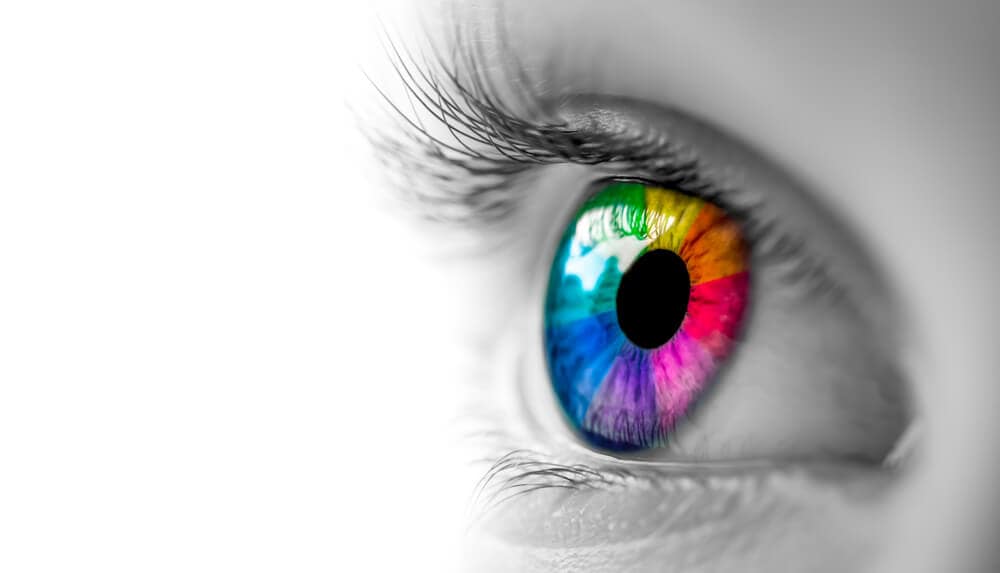

Tetrachromacy
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: Less Than 15%
Likely one of the most useful rare genetic traits anyone could have is tetrachromacy. It is possible that many of the world’s greatest artists had some form of it. This genetic trait affects how a person sees our broad color spectrum. Normal people are born with three cones in our eye to see the spectrum but some are born with a rare fourth cone. This might not seem like a lot, but that extra cone allows them to see and specifically find the difference in up to 100 million colors.
People with three cones, normies, can only see up to 1 million colors. That is a massive difference. This trait can be seen in men, but more often affects women. In fact, it is estimated up to 12% of the world’s female population are tetrachromats. It makes you wonder… if many women are born with this fourth cone, why do we not hear about it more? Apparently, a rogue X chromosome inactivation can shut off the visibility of this fourth cone in some women.
Heart On Opposite Side Of Chest
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: Less Than 1%
It would be irresponsible of us to not first mention some important anatomy information. The heart is NOT on the left side of our chest. Rather, it’s in the middle of our chest. However, it does partially go into the left side with the valves and other critical sections of the heart. Therefore, this is why people tend to believe it is completely located on the left. Just remember the bulk of the heart is mostly in the center. However, some are born with their heart leaning to the right side instead.

This is a genetic trait that is referred to as dextrocardia. Since it is mostly the valves and other portions of the heart leaning to the right, there are no real negative consequences from it. The main heart is still in the middle, of course. Therefore, do not assume someone is from another universe due to their heart being toward the right rather than the left. It is speculated that this has happened for thousands of years, and no one was ever better or worse off from it.

High Altitude Tolerance
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: Less Than 5%
If you are wanting to climb Mount Everest, you’re likely going to have a guide. This will almost always be a member of the Sherpas. They have lived around these Tibetan mountains for generations. They know the mountains well, especially Everest, which is why they guide so many. This is the most dangerous job in the world, but the pay is massive for the Tibetan and Nepalese people. Due to being here for generations, these people have developed a rare genetic trait. They can breathe normally at high altitudes, which normally makes even the most experienced non-native climbers sick.

The gene these native people possess goes back 40,000 years. People known as the Denisovans lived in these mountainous regions, and the generations that followed began to develop their incredible genetics. This supergene they have causes an increase in the oxygen-carrying hemoglobin, allowing the body to distribute oxygen more effectively. People with this gene can perform major manual labor tasks in high altitudes without experiencing oxygen deprivation. They can also breathe well in lower altitudes and still keep their incredible ability when they go back into higher altitudes.

Blue Eye Color
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: Around 8%
Blue eye color is not normal in the slightest and anyone who has this color has a mutation in their genetics. This might sound weird or scary, but it’s not that big of a deal. It began thousands of years ago when people began moving out of civilizations in the Middle East and into colder European sectors. Melanin began to change for these people as they no longer operated as often outdoors due to the far colder temperature. Eventually, the white caucasian skin color came from this.
Yet melanin did not stop with skin color, it also affected hair color and eventually the eyes. When it comes to blue eyes specifically, a genetic mutation in the HERC2 gene is to blame. This mutation causes reduced melanin production in the iris, which can offer a beautiful blue color. However, the lack of melanin also means those with blue eyes will be more sensitive to light. For example, they might need sunglasses in even small sunlight or have trouble driving at night due to lights on the road.
Golden Blood
- Percentage Of People Who Have It: Less Than 0.5% (Only 43 People Have Ever Reported To Have It)
We should state that we do not literally mean blood made of gold or gold-colored blood. Rather, this name typically comes from the rarity of this blood type. It is so rare that most hospitals have only a small supply of it or none at all. The “golden blood” is officially called the RH Null blood type. Basically, those with this blood type are missing all of their RH-blood antigens. Interestingly, anyone with another rare RH blood type can accept this blood type from donors.
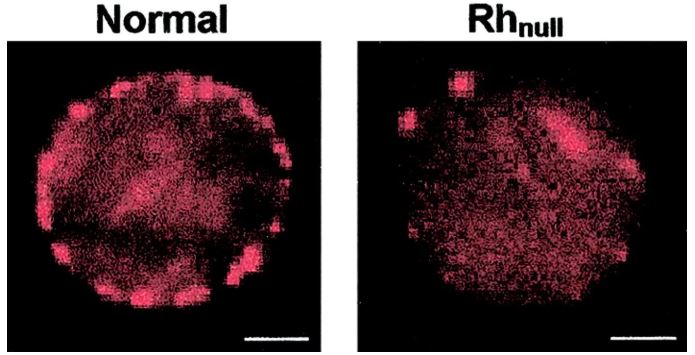
As you can assume, since RH blood types are rare themselves, having RH Null blood around to give to ANY within the RH group is massively valuable. That is why those with this blood type are asked to donate as much blood as they can, as the medical community needs it in hospitals. However, due to the need hospitals have for it, RH Null blood is heavily needed for those who study blood too. If RH Null people did not exist, it could take literally months to years to find a specific RH donor.

